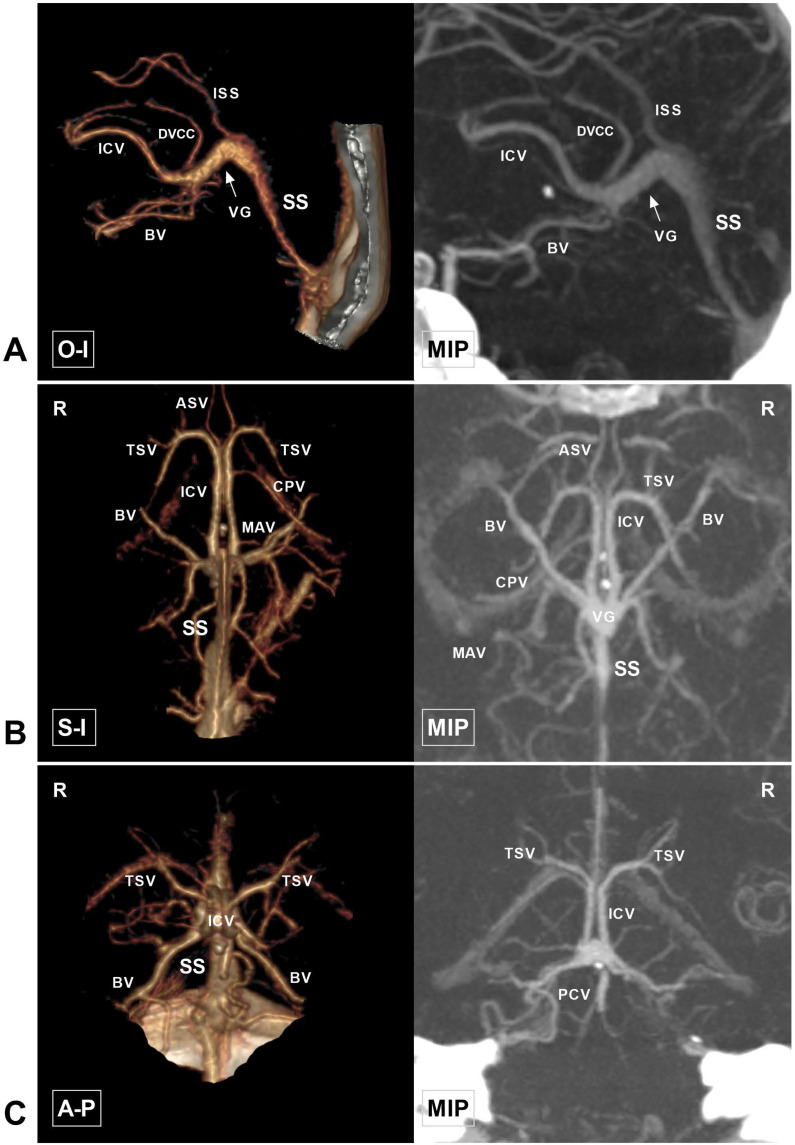
Figure 1.
Anatomy of the cerebral deep vein on CTA. A, CTA and MIP in the O-I view show that the ICV extends backward as the VG (arrow). The VG continues as the SS and empties into the torcular herophili. The DVCC and ISS drain into the VG at their beginning and terminal portions, respectively. B, CTA and MIP in the S-I view show that TSV and ASV merge into the ICV. The bilateral ICVs and BVs merge into the VG and continue as the SS. The CPV and MAV draining into the ICV are also visible. C, CTA and MIP in the A-P view show that the TSV continues as the ICV and then merges with the BV. The PCV draining to the VG is visible. Abbreviations: A-P, anterior to posterior; ASV, anterior septal vein; BV, basal vein; CPV, choroid plexus vein; CTA, computed tomography angiography; DVCC, dorsal vein of the corpus callosum; ICV, internal cerebral vein; ISS, inferior sagittal sinus; MAV, medial atrial vein; MIP, maximum intensity projection; O-I, outside to inside; PCV, precentral cerebellar vein; R, right; S-I, superior to inferior; SS, straight sinus; TSV, thalamostriate vein; VG, vein of Galen.