Fig 2.
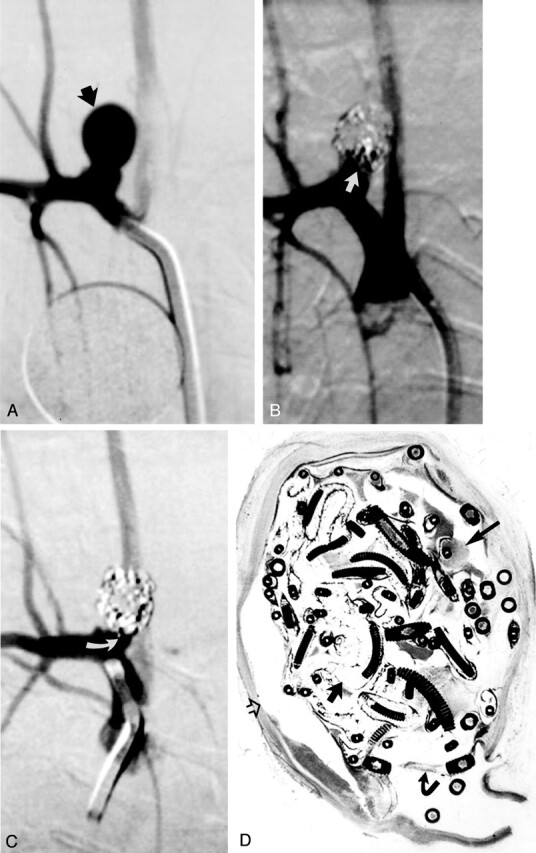
Study animal 4, 2-week implant.
A, Anteroposterior digital subtraction angiogram of the brachiocephalic artery shows a narrow-necked 5.4-mm-wide 7.8-mm-high aneurysm (black arrow).
B, Anteroposterior digital subtraction angiogram obtained immediately after embolization with a single complex coil and three hydrogel devices shows dense packing of the aneurysm dome, with persistent flow at the aneurysm neck (straight white arrow).
C, Anteroposterior digital subtraction angiogram obtained 2 weeks after embolization shows progressive occlusion of the aneurysm cavity, with the neck now occluded (curved white arrow).
D, Hematoxylin and eosin stain; original magnification, ×6.8. Coronal section obtained through the aneurysm cavity. The aneurysm cavity is filled with a mixture of unorganized thrombus (long straight arrow) and expanded hydrogel (short straight arrow). The hydrogel stains as faint, violet-colored, reticular material. There is no substantial inflammation. A thin fibrin membrane traverses the neck (curved arrow). Artifactual separation between the aneurysm wall and the coils and hydrogel occurred during processing (open arrow).
