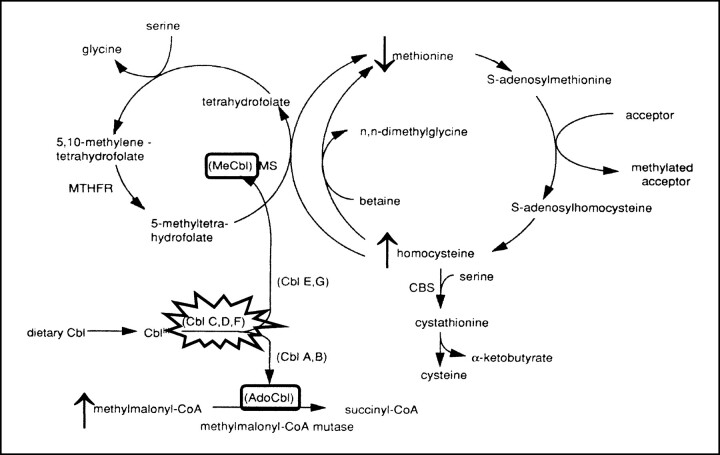
fig 5.
The metabolism of MMA-HC. The disease results from impaired hepatic conversion of dietary cobalamin (Cbl) to both methylcobalamin (MeCbl) and adenosylcobalamin (AdoCbl). Complementation studies individuate three genetic subsets (CblC, CblD, and CblF) within MMA-HC, whereas other complementation groups represent biosynthetic defects that are restricted to either AdoCbl (CblA, CblB) or MeCbl (Cbl E, CblG) and that, as a consequence, represent different diseases. Absence of MeCbl and AdoCbl results in defective activity of methionine synthase (MS) and methylmalonyl-CoA mutase, respectively; the eventual biochemical picture is represented by hyperhomocysteinemia, homocystinuria, hypomethioninemia, methylmalonic acidemia, and methylmalonic aciduria. CBS indicates cystathionine β-synthetase; MTHFR, 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase. Modified from (7) and reproduced with permission from Springer, Berlin