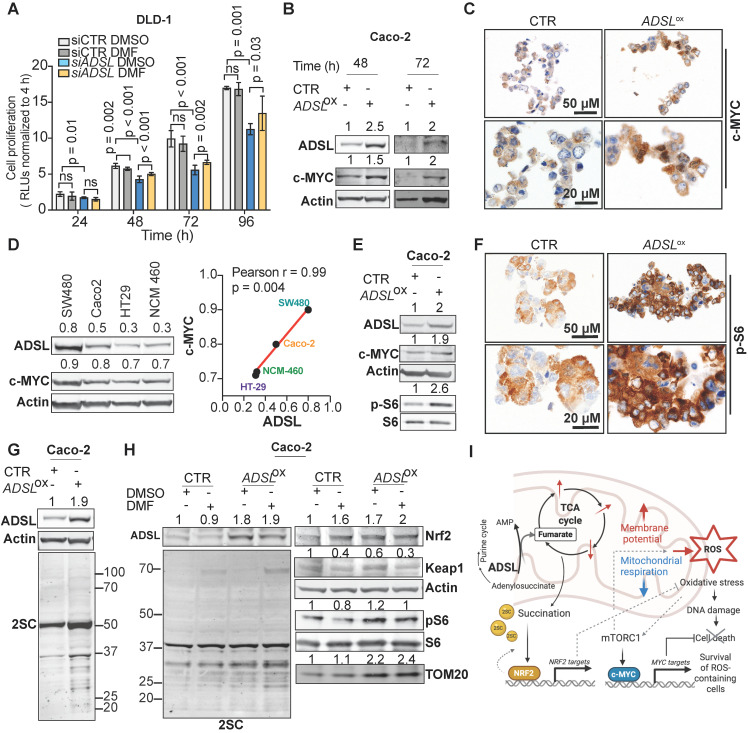
Figure 6.
ADSL overexpression induces succination and mTOR activation and increases c-MYC protein expression. (A) Proliferation capacity of DLD-1 control and ADSL-silenced cells treated with DMSO or fumarate (50 µM). (B) Immunoblot showing ADSL and c-MYC expression in the Caco-2 cells at 48 and 72 h post transfection. (C) Representative pictures of control and ADSL-overexpressing Caco-2 cells immunostained with c-MYC. Scale bars 20-50 µm. (D) Immunoblot showing ADSL and c-MYC expression in CRC cell lines (left). Correlation (linear regression) between c-MYC (Y-axis) and ADSL (X-axis) levels of expression (relative to actin). (E) Immunoblot showing ADSL, c-MYC and phospho and total S6 expression in Caco-2 cells 48 h post-transfection. (F) Representative pictures of control and ADSL-overexpressed Caco-2 cells immunostained with phospho-S6 (p-S6). Scale bars 20-50 µm. (G) Immunoblot showing ADSL and succination (2-SC) levels in Caco-2 cells 48 h post-transfection. (H) Immunoblot showing ADSL and succination (2-SC) levels (left) and KEAP1, NRF2, TOM20, total and phospho-S6 in control and ADSL-overexpressing Caco-2 cells treated with DMSO or fumarate (50 µM). (I) Schematic representation of ADSL-driven pro-oncogenic effects in CRC cells.