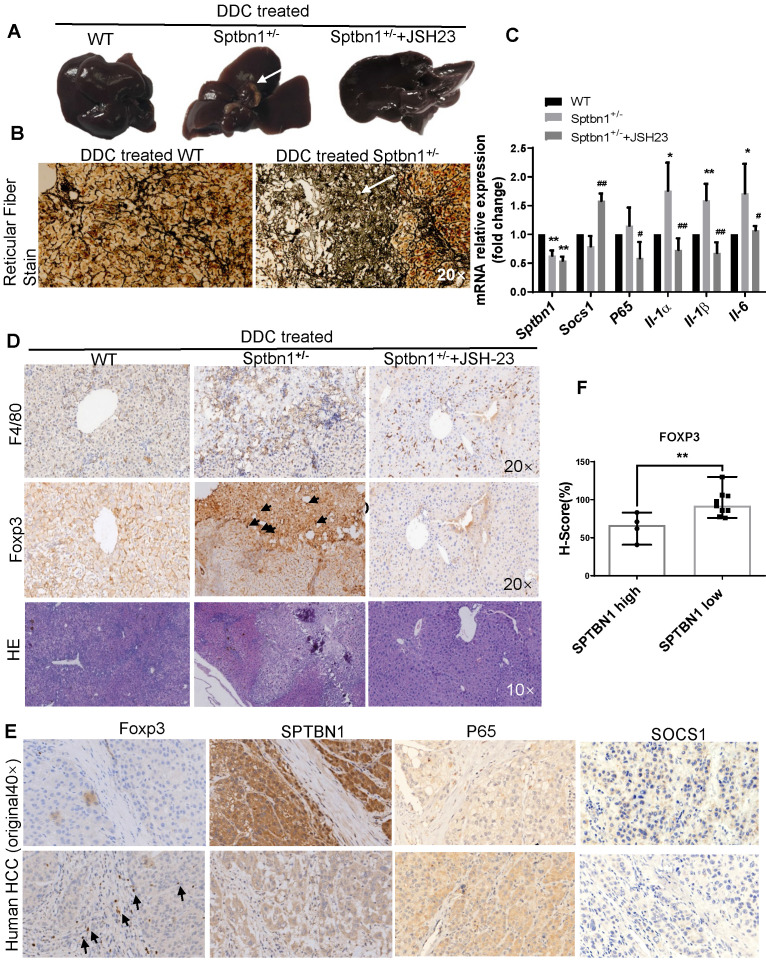
Figure 7.
Loss of SPTBN1 promotes hepatocarcinogenesis and inflammatory through p65 signaling pathway. A. Upon treatment with 0.1% DDC-containing diet for 3 months, Sptbn1+/- mice developed HCC (arrows), compared to WT and JSH-23 (p65 inhibitor) treated Sptbn1+/- mice. B. Liver tissues from WT and Sptbn1+/- mice treated with 0.1% DDC for 3 months were analyzed by Gomori's reticular fiber staining. C. Liver tissues from WT and Sptbn1+/- mice treated with 0.1%DDC in the absence or presence of JSH-23 for 3 months were analyzed by QRT-PCR. The mRNA levels of IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-6, SOCS1 and p65 were detected. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 (WT vs Sptbn1+/-, n = 4). D. IHC and H&E staining. Liver tissues from mice treated same as in Figure 7A were analyzed by immunohistochemistry staining by antibodies targeting macrophages and Treg cells. E. Human HCC tissues were analyzed by immunohistochemistry staining by antibodies against FOXP3, p65, SOCS1 and SPTBN1. F. FOXP3 staining was evaluated by immunohistochemistry score in human HCC. H-score was determined based on the intensity of nuclear staining and the proportion of labeled tumor cells. **P < 0.01 vs SPTBN1 high. n = 13.