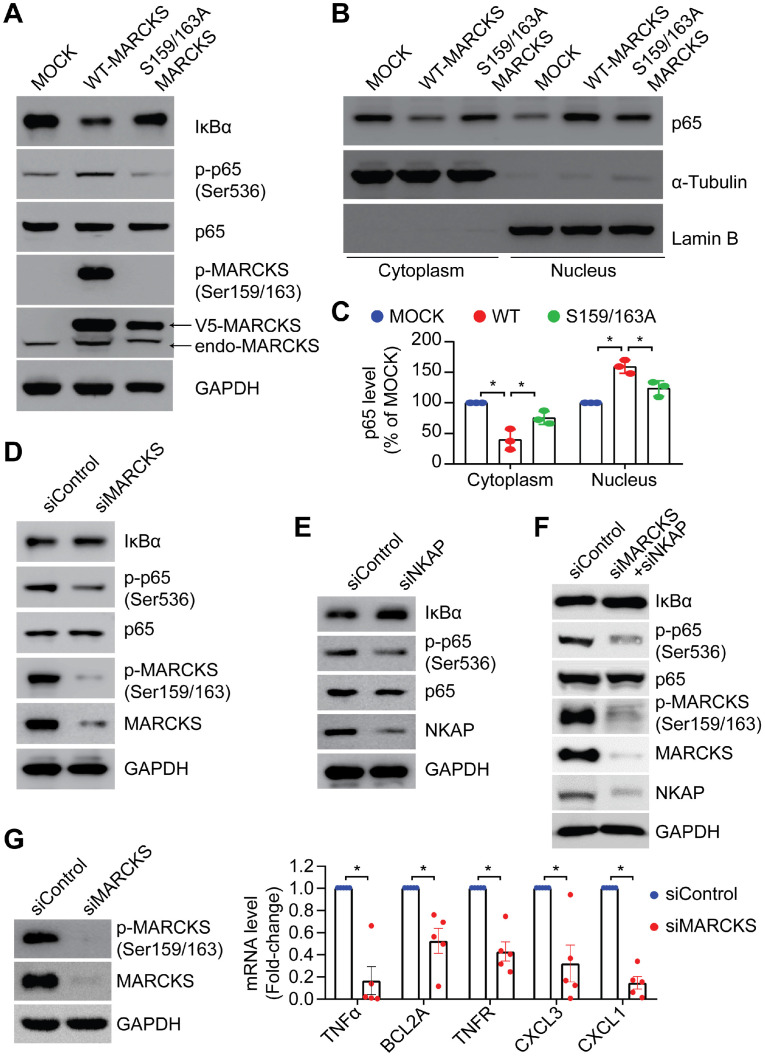
Figure 4.
MARCKS modulates NF-κB singling through NKAP expression. PANEL A-C: Effects of ectopic V5-tagged wild-type or PSD-mutated (S159/163A) MARCKS expression on MARCKS phosphorylation, NF-κB signaling activity (A) and p65 localization (B) in CL1-0 cells. (C) Quantification of western blots for p65 localization in the cytoplasm and nucleus of CL1-0 cells transfected with V5-tagged wild-type MARCKS, V5-tagged S159/163A MARCKS or mock control. Data from three independent experiments are represented as mean ± SD; *, p < 0.05. (D) Effects of MARCKS siRNA silencing on NF-κB signaling activity and MARCKS phosphorylation in CL1-5 cells. (E) Western blot analysis of NF-κB signaling activity upon siRNA knockdown of NKAP expression in CL1-5 cells. (F) Effects of dual knockdown of MARCKS and NKAP on NF-κB signaling activity in CL1-5 cells. (G) Expression of NF-κB target genes in response to MARCKS knockdown. Left, MARCKS protein and its phosphorylation in control siRNA and MARCKS-knockdown CL1-5 cells were determined after 72 hours of siRNA transfection. Right, control siRNA and MARCKS-knockdown CL1-5 cells were harvested for RNA isolation and the level of gene expression was quantified with real-time RT-qPCR and normalized with the TBP level. Data expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 5; *, p < 0.05).