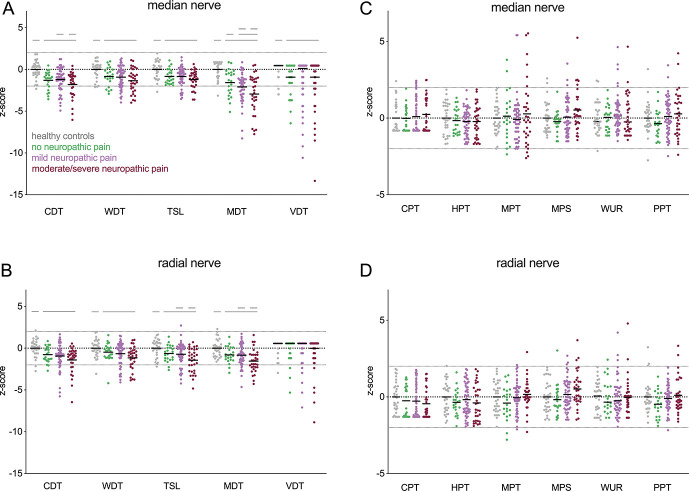
Figure 1.
Somatosensory phenotypes as determined with quantitative sensory testing (QST Z-scores): (A) Detection thresholds in the median nerve territory demonstrating a larger deficit for all detection thresholds in patients with carpal tunnel syndrome compared with healthy controls. Patients with moderate/severe neuP have more pronounced CDT deficits compared to patients with mild neuP. All Helmert contrasts were significant for MDT, suggesting that mechanical deficits intensify with the presence and increasing severity of neuP. (B) Detection thresholds in the radial nerve territory demonstrating a larger deficit in CDT, WDT, TSL, and MDT for patients with carpal tunnel syndrome compared with healthy controls. Patients with moderate/severe neuP have a more pronounced deficit in TSL and MDT compared with those with mild neuP. (C) Pain thresholds in the median nerve territory are comparable among groups. (D) Pain thresholds in the radial nerve territory are comparable among groups. Straight lines represent significant Helmert contrasts. CDT, cold detection threshold; CPT, cold pain threshold; HPT, heat pain threshold; MDT, mechanical detection threshold; MPS, mechanical pain sensitivity; MPT, mechanical pain threshold; neuP, neuropathic pain; PPT, pressure pain threshold; TSL, thermal sensory limen; VDT, vibration detection threshold; WDT, warm detection threshold; WUR, wind-up ratio.