Extended Data Fig. 6. The SQSTM1-INSR pathway mediates CLP-induced polymicrobial sepsis.
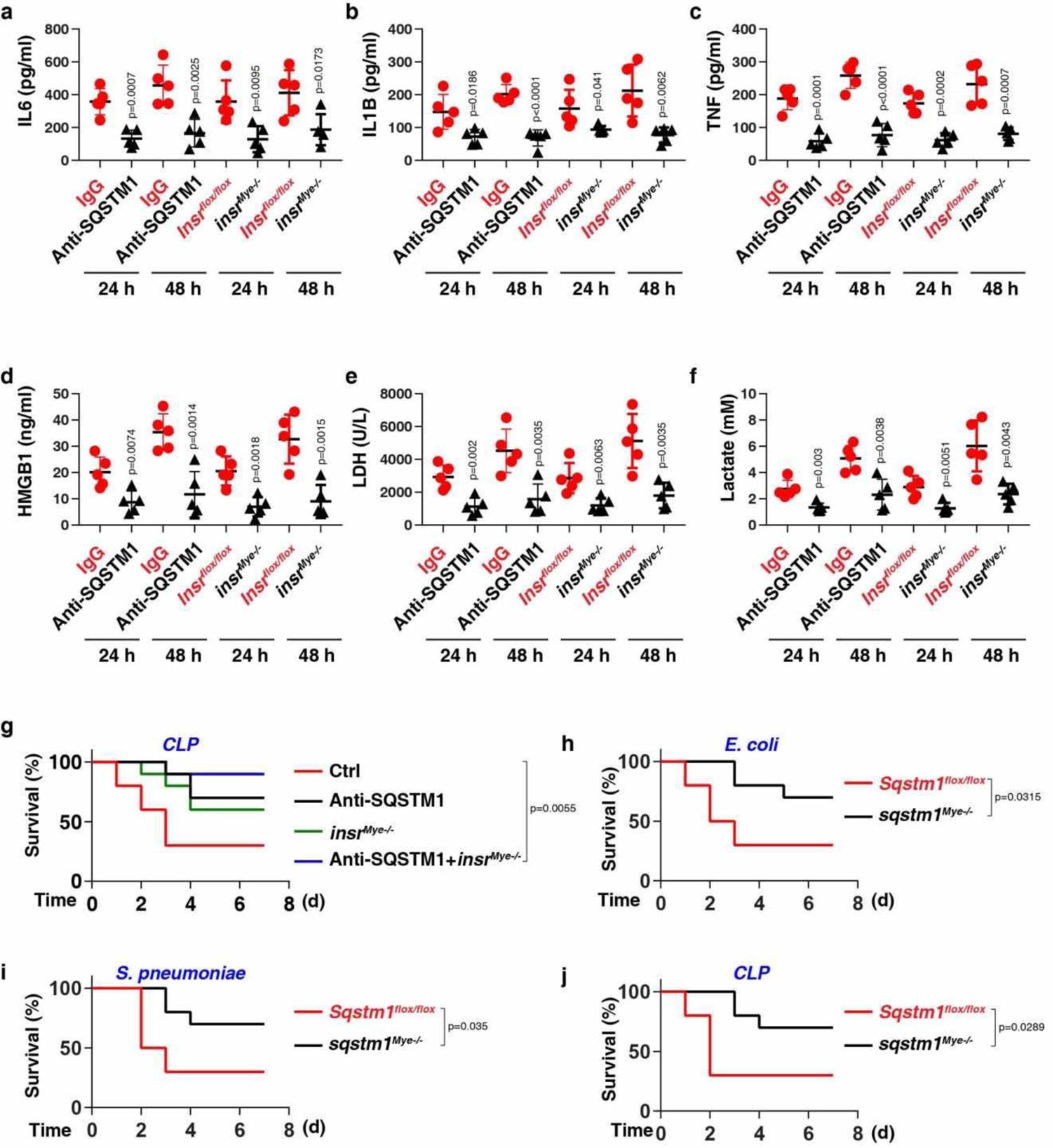
(a-f) The serum level of IL6 (a), IL1B (b), TNF (c), HMGB1 (d), LDH (e), and lactate (f) were assayed in indicated CLP-induced mice with or without anti-SQSTM1 monoclonal antibodies (20 mg/kg) treatment or depletion of INSR in myeloid cells (n = 5 mice/group; two-tailed t test, versus control group). (g) Administration of anti-SQSTM1 monoclonal antibodies (20 mg/kg) and/or depletion of INSR in myeloid cells in mice prevented CLP-induced animal death (n = 10 mice/group; Log-rank test). (h-j) Survival of the indicated mice after E. coli (h) or S. pneumoniae (i) infection or (j) CLP-induced sepsis (n = 10 mice/group; Log-rank test). Data in (a-f) are presented as mean ± SD from three independent experiments. Data in (g-j) are from two independent experiments.
