Figure 17a:
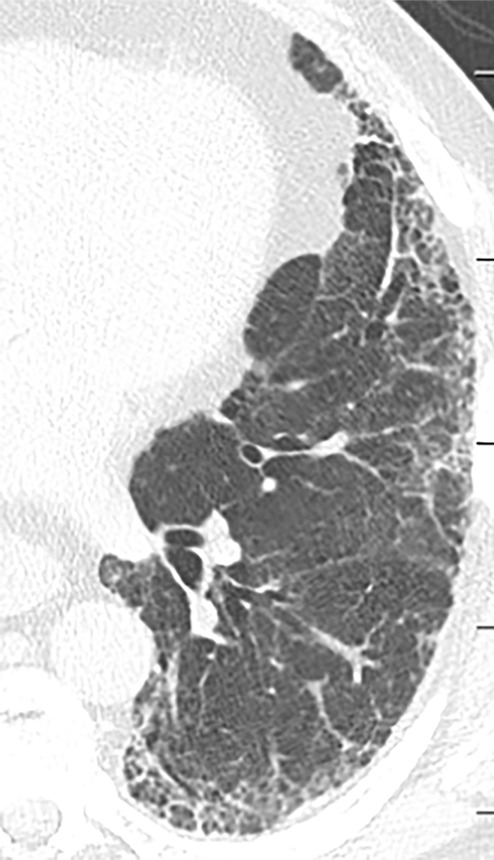
Acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. (a) Zoomed view of axial CT demonstrates a probable usual interstitial pneumonia pattern in a patient with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. (b) Zoomed view of axial CT obtained after rapid deterioration in symptoms demonstrates CT findings of acute exacerbation with progression of reticular abnormality and marked new superimposed ground-glass opacity. Other causes of airspace disease including infection were clinically excluded. (c) Zoomed view of axial CT obtained after resolution of acute exacerbation confirms that the background fibrosis has substantially progressed.
