Fig 1.
A previously healthy 24-year-old man was involved in a traffic crash and presented with severe craniocerebral injuries.
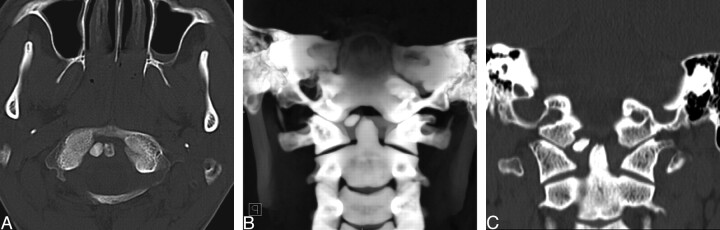
A, Initial axial CT scan shows a nodular calcification between the odontoid tip and the right occipital condyle, suggesting a fractured bone in the craniovertebral junction.
B, 3D volume-rendering image demonstrates a nodular calcification, 7.2 × 7.6 × 4.0 mm, between the occipital condyle and odontoid tip along the course of alar ligament. The bony structures of the craniovertebral junction were normal.
C, Coronal multiplanar reconstruction image shows an attenuated calcific intensity in the region of the right alar ligament, with no remarkable bone marrow component. There is no evidence of fracture in the odontoid process and occipital condyle.