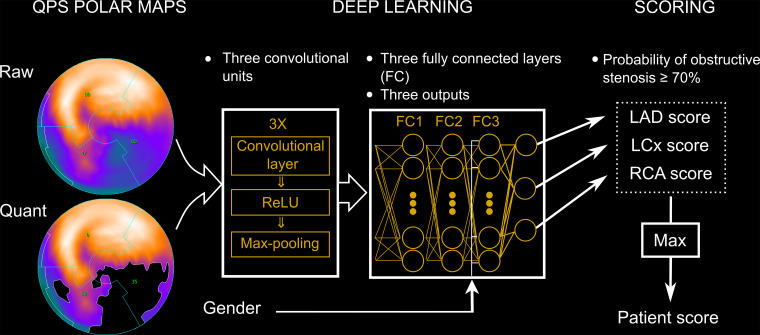
Figure 10:
Deep learning prediction of obstructive coronary artery disease (CAD) from myocardial perfusion imaging. SPECT polar map images are directly connected to the convolutional neural network, and patterns of perfusion defects are identified by feature extraction (left). These image features then pass through three fully connected layers (FC) in a deep learning process (center), which predicts the probability of obstructive CAD in each vascular territory (right). LAD = left anterior descending artery, LCx = left circumflex artery, Max = maximum probability of obstructive CAD, QPS = quantitative perfusion SPECT, ReLU = rectified linear unit (linear function mapping input to output values), RCA = right coronary artery. (Reprinted, with permission, from reference 21.)