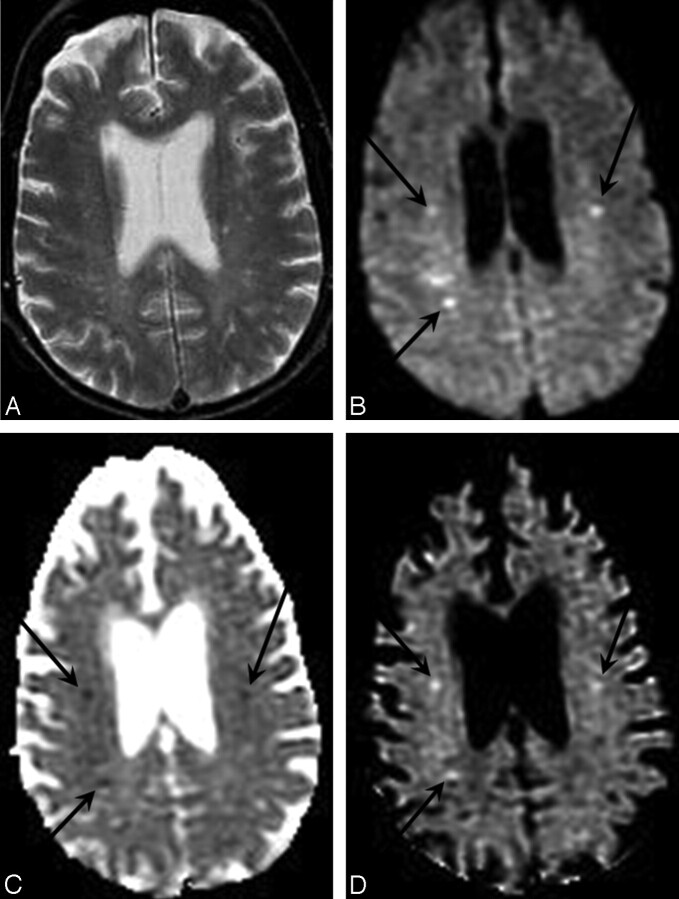
Fig 2.
DWI enables more sensitive and specific diagnosis of acute cerebral ischemia in a case of embolic infarcts due to endocarditis. A, Conventional spin-echo T2-weighted image shows only nonspecific white matter foci of signal hyperintensity. B, Combined DWI image at the same axial level reveals 3 punctuate hyperintense white matter lesions (arrows) that are suggestive of embolic infarcts. C, Corresponding ADC map confirms that there is reduced diffusion in these lesions (arrows), consistent with acute ischemia. D, Attenuation coefficient image, also known as the exponential diffusion image, shows these lesions as remaining hyperintense (arrows). This demonstrates that the hyperintensity on the combined DWI image is not due to T2 shinethrough artifact.