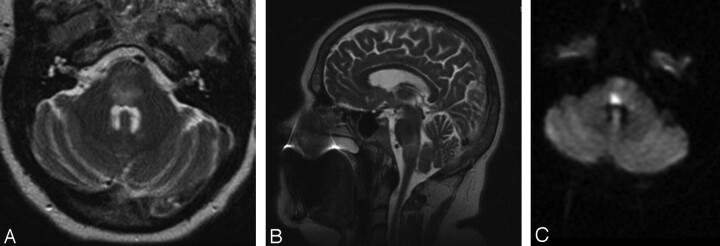
Fig 2.
A–C. Initial MR imaging after a change in the patient's neurologic examination. A, Axial T2-weighted MR imaging demonstrating diffuse edema within the pons. B, Sagittal T2-weighted MR imaging demonstrating the cranial-caudal extent of edema at the pontomedullary junction. C, Axial DWI MR imaging showing a region of restricted diffusion, highly suggestive of infarct, within the dorsal pons.