Fig 1.
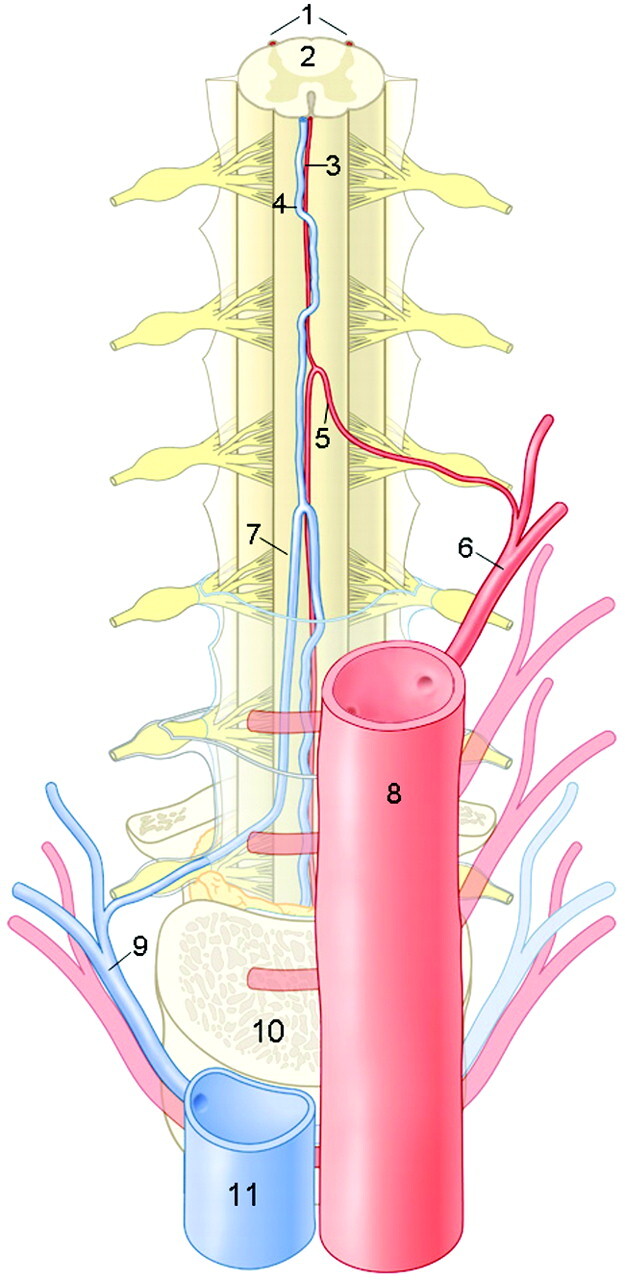
Anatomic drawing of a coronal view on the arteries and veins of the thoracolumbar spinal cord. The largest and, therefore, considered as the most important supplier of the thoracolumbar spinal cord is the Adamkiewicz artery (AKA). This inlet artery, or great anterior radiculomedullary artery, originates from a posterior branch of a segmental artery and courses through a typical hairpin turn to the ASA. The anterior median vein drains the blood from the spinal cord to the radiculomedullary veins. The largest of the outlet veins is the great anterior radiculomedullary vein (GARV), which connects to a segmental vein that eventually merges with the vena cava. Note the anatomic similarities in the configuration between the AKA and the GARV, which both exhibit a hairpin-like (intradural) course. However, the AKA is normally thinner, has a shorter intradural span, and is located more cranially than the GARV. 1 indicates posterior spinal arteries; 2, spinal cord; 3, ASA; 4, anterior median vein; 5, AKA; 6, segmental artery; 7, GARV; 8, aorta; 9, segmental vein; 10, vertebral body; and 11, vena cava. (Illustration made by Rogier Trompert.)
