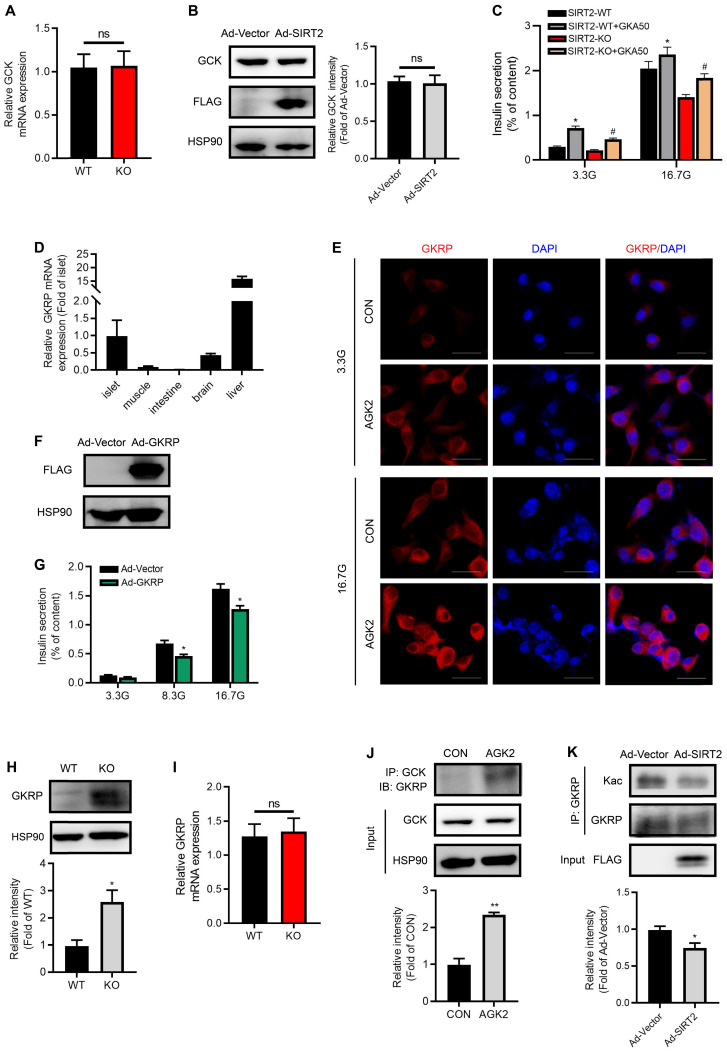
Figure 6.
SIRT2 inhibition stabilizes GKRP protein and enhances its binding to GCK. (A) mRNA levels of GCK in the islets isolated from SIRT2-WT and SIRT2-KO rats (n=3). (B) Protein expression of GCK in INS-1 cells transfected with Ad-SIRT2 or Ad-Vector adenovirus for 36 h. (C) Islets isolated from SIRT2-WT and SIRT2-KO rats were incubated with 3 µM GKA50 in the presence of 3.3 or 16.7 mM glucose for 1 h, and insulin secretion was assayed (n=4). (D) mRNA levels of GKRP in different tissues (n=6). (E) INS-1 cells treated with 3 μM AGK2 for 6 h in the presence of 3.3 or 16.7 mM glucose were stained by immunofluorescence for GKRP (red) and nuclei (DAPI, blue) (bar=20 μm). (F) Protein level of GKRP in rat islets transfected with Ad-Vector or GKRP-overexpressing adenovirus (Ad-GKRP). (G) Rat islets transfected with Ad-Vector or Ad-GKRP adenovirus were stimulated with 3.3, 8.3 or 16.7 mM glucose for 1 h, and insulin secretion was assayed (n=4). (H-I) Protein and mRNA expressions of GKRP in the islets isolated from SIRT2-WT and SIRT2-KO rats (n=3). (J) The interaction between GCK and GKRP was detected in INS-1 cells treated with 3 μM AGK2 for 6 h. (K) After INS-1 cells were transfected with Ad-Vector or Ad-SIRT2 adenovirus, cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with GKRP antibody and subjected to Western blot with anti-acetyllysine antibody. Data are expressed as means ± SEM. *P< 0.05, **P< 0.01 vs control group. #P< 0.05 vs SIRT2-KO group.