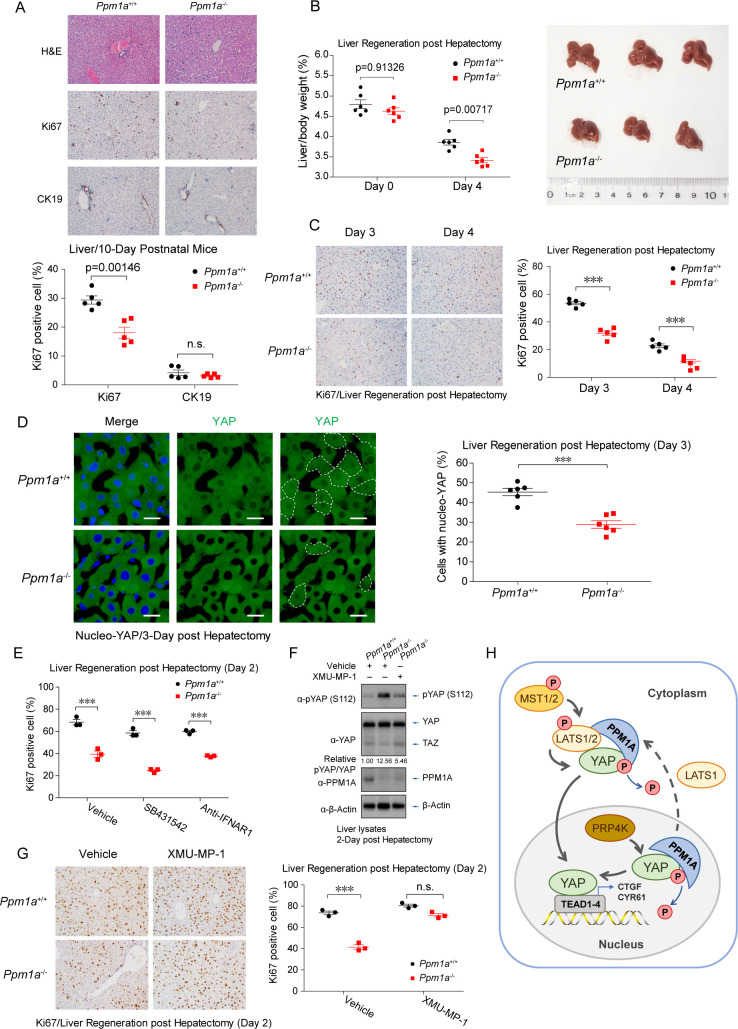
Fig 7. PPM1A deficiency impedes the liver regeneration.
(A) H&E staining of liver sections from the 10-day postnatal mice showed a reduced level of hepatocyte proliferation (Ki67 positive) but an elevated level of immune cell infiltration and vacuoles in PPM1A KO mice. (B) Wild-type and PPM1A KO mice at 8–10 weeks age were carried out with hepatectomy surgery. The ratio of liver/body weight was measured at day 4 post hepatectomy, which exhibited a marked decrease of compensatory liver regeneration in Ppm1a−/− mice. n = 6 mice in each group. (C) A compromised level of hepatocyte proliferation in compensatory liver regeneration of Ppm1a−/− mice was detected by Ki67 staining examined at day 3 and day 4 post hepatectomy. (D) Immunofluorescence imaging of liver sections revealed a dramatic decrease of the nucleo-YAP in livers from Ppm1a−/− mice examined at day 3 post hepatectomy, exhibiting by the fewer YAP proteins in the nucleus (darker imaging in the nucleus, left panel) and the substantially lesser cells with the nucleo-YAP localization (circled, and right panel). (E) Administration of SB431542 or anti-IFNAR1 failed to restore the suppressed hepatocyte proliferation in compensatory liver regeneration in Ppm1a−/− mice, examined at Day 2. (F, G) Administration of MST inhibitor XMU-MP-1 decreased the level of phospho-YAP (S112) (F) and increased the proliferating hepatocyte (G) in Ppm1a−/− livers. (H) A schematic model for the PPM1A-regulated Hippo-YAP signaling. PPM1A associates with YAP/TAZ both in the cytoplasm and in the nucleus and directly eliminates the key phosphorylation modifications on YAP, which determines the nucleocytoplasmic localization and transcription potency of YAP/TAZ. Accordingly, PPM1A functions as a critically physiological regulator of the Hippo-YAP pathway in mammals, including the intestinal and liver regeneration upon injuries. Unprocessed images of blots are shown in S1 Raw Images. Statistics source data are provided in S1 Data. H&E, hematoxylin and eosin; KO, knockout; MST, mammalian sterile 20-like kinase; phospho-YAP, phosphorylating forms of YAP; PPM1A, protein phosphatase magnesium-dependent 1A; TAZ, transcriptional coactivator with PDZ-binding motif; YAP, Yes-associated protein.