Fig. 2. Tau-targeted ZFP-TFs reduce tau mRNA and protein expression in vivo.
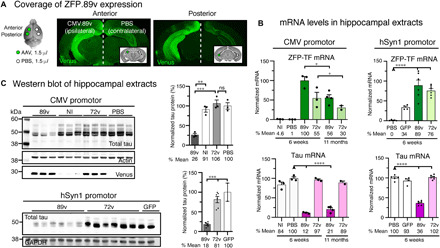
(A) Location of hippocampal injection sites and subsequent ZFP-TF.89v expression in the mouse brain. The left hemisphere received two 1.5-μl injections of AAV9 CMV.89v (CMV.72v) into the anterior and posterior hippocampus, and the right hemisphere received two injections of PBS of the same volume into the same coordinates. Some hippocampi did not receive an injection and served as noninjected (NI) controls. Representative images of coronal brain sections show the widespread expression of the Venus reporter protein in the left hippocampus. Venus labeling in the right hemisphere results from contralateral projections of CMV.89v-transduced neurons in the left hippocampus. (B) mRNA levels of ZFP-TF (ZFP; green) and tau (pink) in CMV.89v- and hSyn1.89v-injected hippocampi. After 6 weeks, CMV.89v reduces tau mRNA down to 12% (by 88%) and hSyn1.89v down to 36% (by 64%), whereas control CMV.72v- or hSyn1.72v-injected hippocampi have the same amount of tau mRNA as noninjected and PBS-injected mice. After 11 months, tau was still reduced by 80% in CMV.89v hippocampi. Data are presented as means ± SEM. One-way ANOVA with Sidak’s test for multiple comparisons, reference for significance indicated by arrowhead, n = 3 mice per group. (C) Tau protein reduction in hippocampal extracts of CMV.89v- and hSyn1.89v-injected animals demonstrated by Western blot of lysates 6 weeks p.i. CMV.89v reduced total tau protein expression by ~74% and hSyn1.89v by ~82%. CMV.72v, noninjected, and PBS-injected hippocampi had similar tau protein levels. One-way ANOVA with Sidak’s posttest, n = 3 mice per group.
