Fig. 6. Chemogenetically increased neuronal activity in S1HL was associated with a decrease of the threshold of pain.
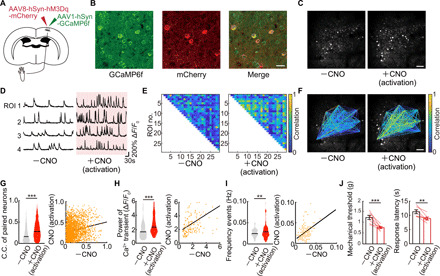
(A) Schematic diagram showing virus injection. WT mice were injected with AAV1-hSyn-GCaMP6f and AAV8-hSyn-hM3Dq-mCherry into the hindlimb region of primary somatosensory cortex (S1HL) to enable in vivo Ca2+ imaging and increased neuronal activity in S1HL neurons by administered CNO. (B) Immunostaining image of S1HL neurons. Left, GCaMP6f; middle, mCherry; right, merged image. Scale bar, 20 μm. (C) Representative example of images of the same neurons before and after a single dose of CNO. Scale bar, 100 μm. (D) Representative calcium traces of typical four neurons. Each neuronal activity was traced from before to after a single dose of CNO. (E and F) Representative example of paired neuronal C.C. from before to after a single dose of CNO. Scale bar, 100 μm. (G to I) Change in C.C. of paired neurons, pCa2+, and frequency of Ca2+ transients (n = 2292 pairs, 151 neurons per five mice) in before and after a single dose of CNO. **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001; paired t test. Violin plots show median (black lines) and distribution of the data. (J) Change in pain threshold before and after a single dose of CNO (n = 7 mice). **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001; paired t test. Error bars show means ± SEM.
