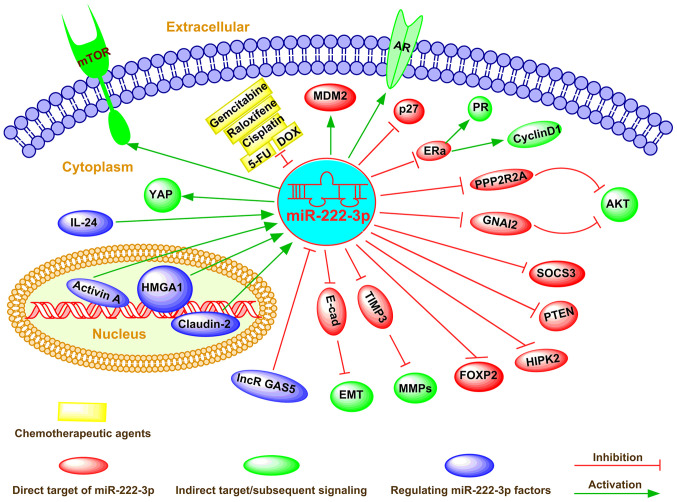
Figure 2.
Emerging roles and mechanisms of miR-222-3p in human cancer. miR-222-3p can directly or indirectly regulate multiple downstream pathways, such as PI3K/AKT, PTEN, JAK/STAT, TRPS1/ZEB1 and EMT, between which crosstalks usually exist, thus constituting a complex signaling network. Additionally, miR-222-3p can extensively regulate multiple cell functions, including differentiation, proliferation, apoptosis, invasion, metastasis and metabolism modulation via targeting gene expression at the post-transcriptional level. Furthermore, miR-222-3p serves an important role as either a tumor suppressor or an oncogene in different types of cancer. Dysregulated miR-222-3p expression contributes to drug resistance and has been emphasized as a new drug target. In addition, miR-222-3p expression can be regulated via both transcriptional factors and epigenetic factor-induced mechanisms in cancer cells. AR, androgen receptor; DOX, doxycycline; EMT, epithelial-mesenchymal transition; E-cad, E-cadherin; ERa, estrogen receptor α; FOXP2, forkhead box protein P2; GNAI2, G protein α inhibiting activity polypeptide 2; HIPK2, homeodomain-interacting protein kinases 2; HMGA1, high mobility group AT-hook 1; lncR GAS5, long non-coding RNA growth arrest-specific 5; MDM2, murine double minute 2; miR, microRNA; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; PPP2R2A, phosphatase 2A subunit B; PR, progesterone receptor; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homology deleted on chromosome ten; SOCS3, suppressor cytokine signaling 3; YAP, Yes-associated protein; 5-FU, 5-fluorouracil.