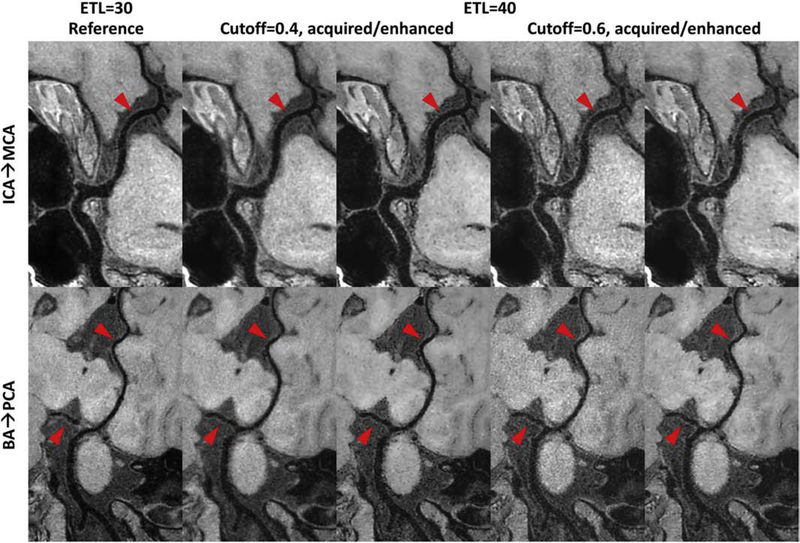
Figure 4:
Comparison of curved planar reformatted (CPR) images for different 3D turbo spin echo (TSE) intracranial vessel wall imaging sequences. Column 1 shows the reference image acquired with an echo train length (ETL) 30, while other columns are images acquired with ETL 40 but using different cutoff values to design the TSE refocusing pulse train (cutoff = 0.4 for column 2 and 3, cutoff = 0.6 for column 4 and 5). Column 2/4 shows the acquired CPR image, and column 3/5 shows the convolutional neural network enhanced CPR image. The top CPR images cover from the left C6 segment of internal carotid artery (ICA) to the M1 segment of middle cerebral artery (MCA), while the bottom CPR images cover from the end of right vertebral artery to the right posterior cerebral artery (PCA). Note the reduced noise level in brain tissue regions and the improved vessel wall delineation in column 3/5 shown by the red arrows compared to column 2/4.