Figure 5.
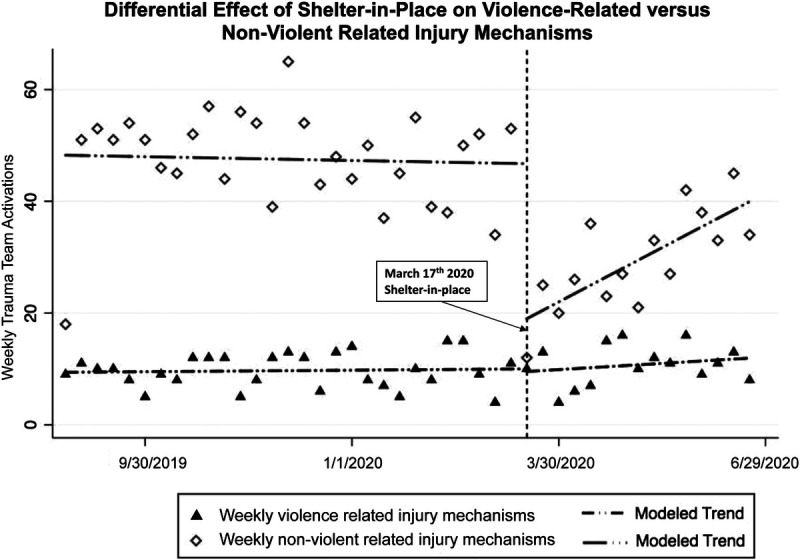
Comparison of weekly violence-related vs. nonviolent injury mechanisms before and after shelter-in-place. ITSA model for violence-related versus nonviolent injury mechanisms at weekly intervals, lags specified for autocorrelation: 4 weeks. While pre–shelter-in-place trends for both violence-related and nonviolent injury mechanisms was stable, a large difference in level shift is notable in association with shelter-in-place for nonviolent injury mechanisms, but there was no level change in violence-related injury mechanisms (p < 0.01). After shelter-in-place, a gradual and significant increase in nonviolent injury mechanisms was noted (p < 0.01), but no significant change (slight upward trend) in violence-related injury mechanisms. See Supplemental Table 5B (http://links.lww.com/TA/B859) for complete ITSA model results.
