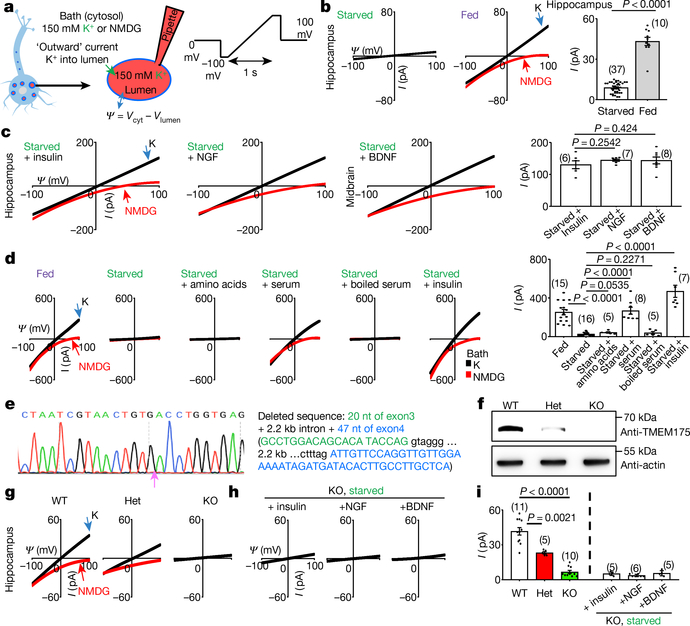
Fig. 1 |. A growth-factor-activated lysosomal K+ channel, lysoKGF.
a, Schematic of the recording of neuronal lysosomes. b, Currents (I) recorded at varying voltages (Ψ) from mouse hippocampal neurons with (starved) or without (fed) overnight starvation in DMEM containing no B27 nutrient. c, Currents from neurons with starvation followed by refeeding (in DMEM medium) with insulin (100 nM for 4 h), NGF (100 ng ml−1, 3 h) or BDNF (10 ng ml−1, 3 h). d, Reconstituting lysoKGF by TMEM175 transfection in HEK293T cells. Currents were recorded before, 2 h after starvation or after a 2-h starvation followed by refeeding with amino acids (10× for 10 min), with serum (10%, 4 h), with serum inactivated by boiling for 10 min or with insulin (100 nM, 4 h). e–i, Comparison between lysoKGF from wild-type and TMEM175-knockout neurons. e, Sequencing of the knock out, showing deletion of parts of exons 3 and 4. f, Total brain proteins (100 μg) from wild type (WT), heterozygous (het) and homozygous TMEM175-knockout (KO) mice were immunoblotted with anti-TMEM175 and—as a loading control—reblotted with anti-actin. For gel source data, see Supplementary Fig. 1. g, Currents from B27-replete hippocampal neurons. h, Currents from B27-starved (overnight in DMEM) knockout neurons refed with insulin (hippocampal neurons), NGF (hippocampal) or BDNF (midbrain). Black (K) and red (N-methyl-D-glucamine (NMDG)) traces are currents recorded with bath solutions containing K+ or NMDG, respectively. Averaged IK sizes (at 100 mV, with K+-containing bath) are in bar graphs (b–d, i). Data are mean ± s.e.m. Numbers of recordings are in parentheses. P values shown are from unpaired two-tailed t-tests.