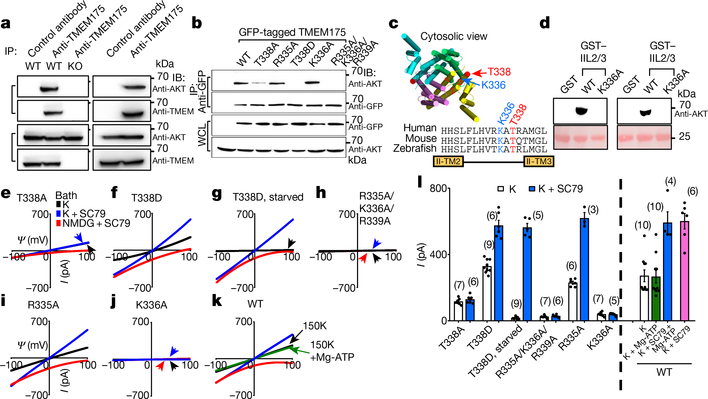
Fig. 3 |. AKT activates TMEM175 via catalysis-independent and interaction-dependent mechanisms.
a, Association between native TMEM175 and AKT. Top two panels, total proteins prepared from wild-type and TMEM175-knockout mouse brains (lanes 1–3) or SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells (lanes 4 and 5) were immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-TMEM175 or with a control antibody (anti-UNC79) and blotted with anti-AKT and anti-TMEM175. Bottom two panels, total protein blotted for input control. b, Lysates from HEK293T cells transfected with GFP-tagged wild-type or mutant TMEM175 were immunoprecipitated with anti-GFP and blotted with anti-GFP or with anti-AKT. Whole-cell lysates (WCL) were also blotted for input control. c, Sequence alignment of the T338 region. The locations of T338 and K336 are indicated on the human TMEM175 structure (Protein Data Bank code (PDB) 6WCA). d, Pull down of AKT with human TMEM175–glutathione-S-transferase (GST) fusion protein. Cell lysates from human AKT1-transfected HEK293T (lanes 1–3) or S2 (lanes 4–6) cells were incubated with glutathione-agarose-bound GST (as a negative control), GST fusion protein of the 19 amino acids of human TMEM175 containing the wild-type TM2–TM3 linker of domain II (GST–IIL2/3; sequence: HHSLFLHVRKATRAMGLLN) or that with the K336A substitution. Top, bound proteins were probed with anti-AKT (top). Bottom, GST fusion proteins were visualized with Ponceau-S staining of the membrane after immunoblotting. e–j, Currents recorded from HEK293T cells transfected with TMEM175 mutants as indicated with (g) or without starvation (wild type shown in Fig. 2d–f). k, Currents recorded with or without Mg-ATP (2 mM) in the bath. l, Averaged IK sizes (at 100 mV) recorded under conditions as indicated. Data are mean ± s.e.m. Numbers of recordings are in parentheses. In e–k, arrows are used to indicate curves that overlap and are not easily distinguished. For gel source data, see Supplementary Fig. 1.