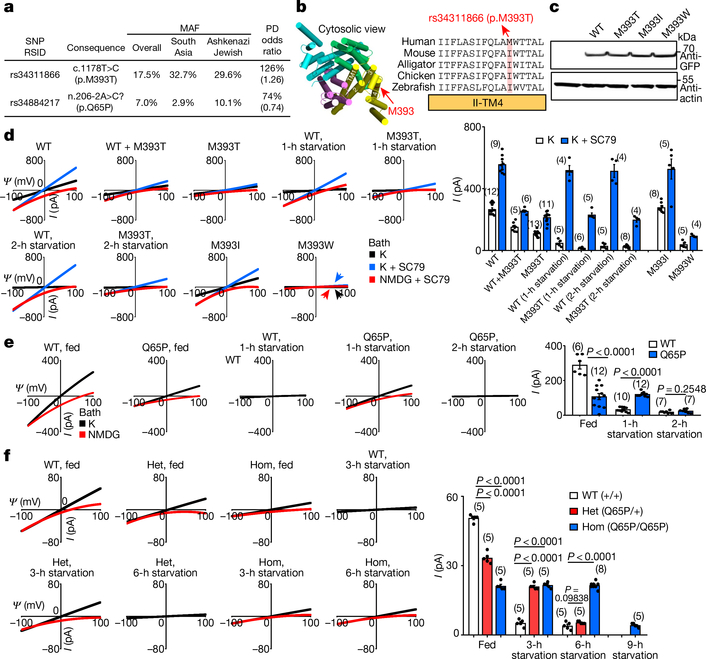
Fig. 4 |. Common TMEM175 variants associated with susceptibility to Parkinson’s disease bidirectionally regulate function of the lysoKGF channel.
a, Variants in human TMEM175 with minor allele frequency (MAF) > 5% (from https://gnomad.broadinstitute.org/). The two single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) are associated with increased (rs34311866, meta-analysis odds ratio 1.26, 95% confidence interval [1.22, 1.31], P = 6.00 × 10−41) or decreased (rs34884217, odds ratio 0.74, 95% confidence interval [0.69, 0.81], P = 1.56 × 10−12) susceptibility to Parkinson’s disease (PD)25 (data from http://www.pdgene.org/). b–d, Characterization of p.M393T. b, Sequence alignments of M393 region (indicated on structure PDB 6WCA). c, Protein expression levels of wild type and human TMEM175 mutants. Total protein from nontransfected HEK293T cells (lane 1) and cells transfected with GFP-tagged wild-type or mutant human TMEM175 (lanes 2–5) was probed with anti-GFP or anti-actin (for input control). For gel source data, see Supplementary Fig. 1. d, Currents from HEK293T cells transfected with wild-type and/or mutant TMEM175 with or without starvation in HBSS medium for 1 or 2 h, as indicated. e, f, Characterization of the TMEM175(Q65P) variant in HEK293T cells (e) and knock-in mouse neurons (f). e, Currents from wild-type and TMEM175(Q65P) cDNA-transfected HEK293T cells before (0 h, fed) or after (1 or 2 h) starvation. f, Currents from wild-type (+/+), heterozygous (Q65/+, het) and homozygous (Q65P/Q65P, hom) knock-in mouse midbrain neurons before (0 h, fed) or after (3, 6 or 9 h) starvation in DMEM. In d–f, averaged IK sizes (at 100 mV) are shown in the bar graphs. Data are mean ± s.e.m. Numbers of recordings are in parentheses. P values shown are for unpaired two-tailed t-tests.