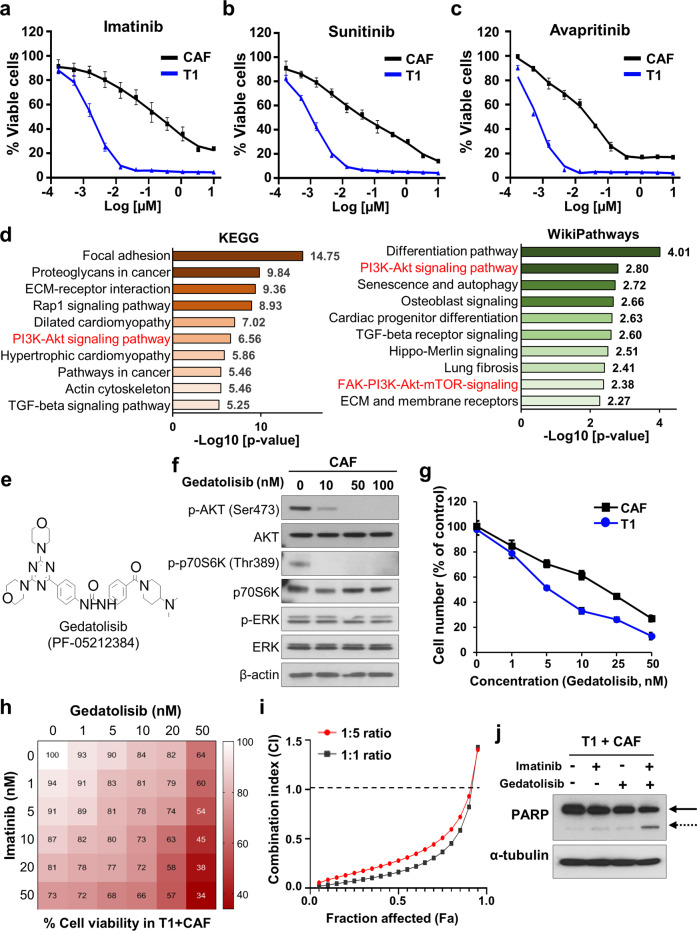
Fig. 6. GIST-CAFs are sensitive to the dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor gedatolisib.
Cell viability assay of T1 cells and GIST-CAFs with the FDA-approved drugs (imatinib, (a); sunitinib, (b); and avapritinib, (c)) for GIST therapy. The viability was detected by colorimetric analysis. d ENRICHR pathway analysis from RNA-seq shown in Fig. 2. The enhanced pathways in the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG; left) and WikiPathways database (right) are shown. Combined score was indicated as a value of -log10 (p value). e The chemical structure of gedatolisib, a dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor, also known as PF-05212384 (Pfizer). f Immunoblotting analysis of p-AKT (Ser473), AKT, p-p70S6K (Thr389), p70S6K, p-ERK, ERK, and β-actin (as a loading control) after GIST-CAFs were treated with gedatolisib (0–100 nM) for 3 h. g The effect of gedatolisib on proliferation of GIST-CAFs and T1. The cells were counted with a TC20™ Automated Cell Counter after treated with gedatolisib (0–50 nM) for 72 h. h, i Combination drug treatment using imatinib and gedatolisib in T1 cells mixed with CAFs. After T1 cells were plated in a 96-well plate with CAFs at 5:1 ratio, the cell mixtures were treated with imatinib and/or gedatolisib for 72 h. Shown were factorial dose matrix (h) and Fa-CI curves generated from CompuSyn software (i). Combination index, CI; Fraction affected, Fa. j Immunoblotting analysis of cleaved poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP)/full length PARP and α-tubulin (as a loading control) after the mixture of T1 and CAFs was treated with imatinib (10 nM), gedatolisib (50 nM), or combination treatment for 72 h. Solid arrow, full length PARP; dashed arrow, cleaved PARP.