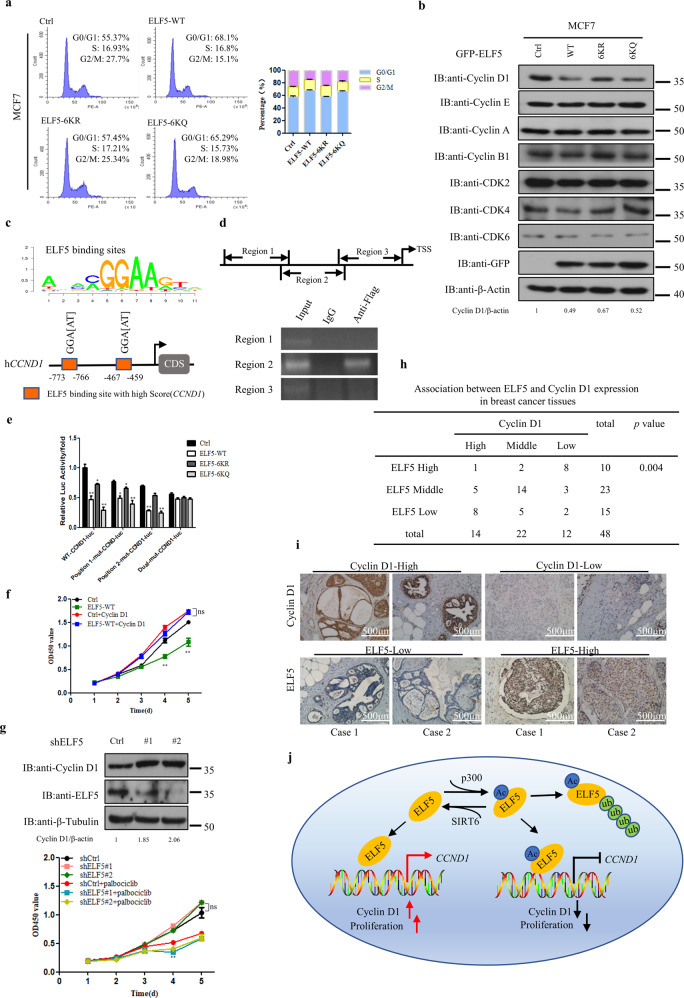
Fig. 7. Inhibition of CCND1 transcription by ELF5 acetylation.
a Flow cytometry analysis of the cell cycle showing the distribution of MCF7 cells stably transfected with GFP-ELF5 WT, GFP-ELF5 6KR, GFP-ELF5-6KQ or control vector. b Western-blot detection of cyclins and CDKs expression in MCF7 cells that overexpressed with GFP-ELF5 WT, GFP-ELF5 6KR, GFP-ELF5-6KQ or the control vector. c Schematic representation of the conserved ELF5-binding motif and on CCND1 potential promoter region. d Regions of CCND1 promoter physically associated with ELF5 as analyzed by ChIP assay. Top: schematic illustration of the PCR-amplified fragments of CCND1 promoter; bottom: ChIP assay was carried out using anti-Flag antibody to screen for ELF5-bound CCND1 promoter regions in HEK293T cells. e Effect of mutations within the ELF5-binding site of CCND1 promoter on its activity. CCND1 promoter with a site-specific mutation within the ELF5-binding site was fused to a luciferase reporter gene. MCF-7 cells transfected with such construct and either Flag-ELF5 WT, Flag-ELF5 6KR, Flag-ELF5-6KQ or the vector pEGFP-C1 were subjected to luciferase activity assay. Data are the means ± SDs from three determinations. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01. f Growth curves of MCF7 cells that stably overexpressed with GFP-ELF5 without or with HA-cyclin D1 overexpression as measured by CCK8 assay. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ns, no significance, compared with cells transfected with just the pEGFP-C1 vector. g Top: T47D cells expressing a shCtrl or shELF5 were analyzed for Cyclin D1 protein level. Bottom: Growth curves of T47D cells expressing a shCtrl or shELF5 without or with palbociclib treatment as measured by CCK8 assay. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ns, no significance. h Correlation between Cyclin D1 and ELF5 expression in breast cancer tissues. Two-side χ2-test was used for statistical analysis. i Representative images of tissue samples from breast cancer patients showing the expression levels of ELF5 and Cyclin D1 as assessed by immunohistochemistry. Both ELF5 and Cyclin D1 levels were classified as low, medium, or high based on the intensities of the IHC staining. j Proposed model depicting the regulation of ELF5 by acetylation. In this model, ELF5 is acetylated by acetyltransferase p300 and deacetylated by deacetylase SIRT6. Acetylation of ELF5 increases its capacity to suppress breast cancer proliferation by suppressing the transcription of its target gene CCND1.