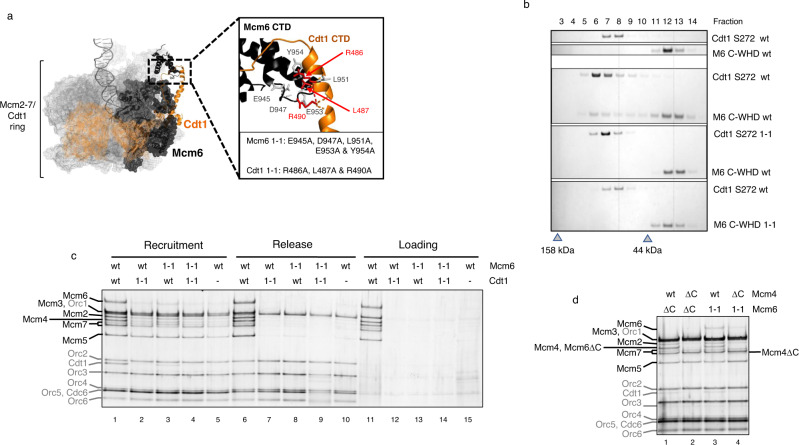
Fig. 4. Stabilization by Cdt1 requires interaction with Mcm6 C-WHD.
Characterization of the Cdt1 and Mcm6 subunits which contain mutations that affect their interaction via their C-WHDs. These mutations were originally described by Liu et al. and here are named 1-1 mutations. a MCM-Cdt1 structure in the recruited OCCM complex (PDB: 5V8F). Mcm2-7 subunits are represented in grey mesh, except Mcm6 that is represented in black, while Cdt1 is represented in orange. Only the secondary structure of the C-WHDs of Mcm6 and Cdt1 is illustrated (in black and orange, respectively). The zoomed area shows the residues substituted in the 1-1 mutations. b The interaction between Cdt1 and Mcm6, either wt or 1-1 mutations, is assessed by gel filtration. To see a bigger shift in the gel filtration profile, here we have used the Cdt1 S272 truncation (described in Fig. 3) and the Mcm6 C-WHD, either wt or 1-1 mutations. The peak fraction of two molecular weight markers is shown as a grey triangle (158 and 44 kDa). c PreRC assay of the MCM-Cdt1 complex, containing Mcm6 and Cdt1 wild type (wt) or 1-1 mutations (1-1). Omission of Cdt1 is used as negative control (lanes 5, 10 and 15). d Recruitment of MCM-Cdt1 containing an Mcm6 subunit with either 1-1 mutation (lanes 3 and 4) or a deletion of its C-WHD (∆C, lanes 1 and 2), in combination with Mcm4 wt or with its C-WHD deleted (∆C). Note that the Mcm4∆C and Mcm6∆C subunits are of reduced size and respectively migrate near Mcm7 and Mcm4 on SDS-PAGE.