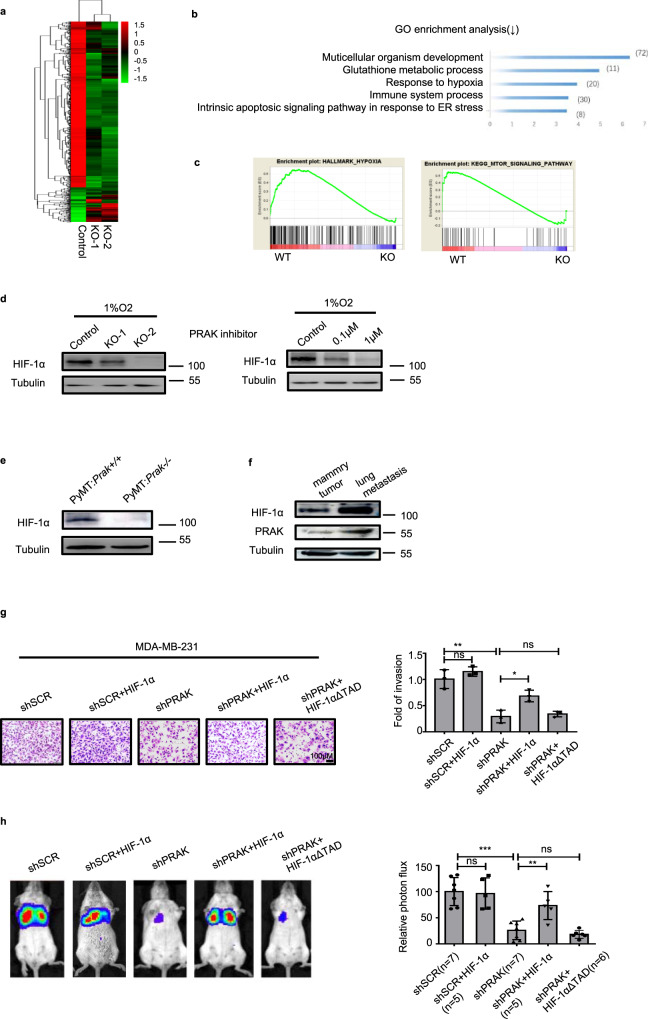
Fig. 4. The metastasis-promoting effect of PRAK is mediated by HIF-1α.
a The transcriptional profiles of parent and Prak knockout B16 clones were determined by RNA-Seq. The heatmap shows the clustering of the differentially expressed genes. b The top five biological functional pathways revealed by GO analysis of the differentially expressed genes. c The coordinated downregulation of gene sets related to hypoxia (NES = 1.4548125, NOM p-val = 0.0) and mTOR signaling (NES = 1.12915, NOM p-val = 0.0) in Prak−/− cells as revealed by GSEA analysis. d Western blotting analysis of HIF-1α levels in Prak+/+ and Prak−/− B16 cells cultured in 1%O2 for 12 h in the presence or absence of GLPG0259. The experiments were repeated 3 times with similar results. e HIF-1α levels in mammary tumor tissues isolated from Prak+/+ and Prak−/− PyMT mice. f PRAK and HIF-1α levels in mammary tumors in comparison to metastatic lesions in the lung isolated from the same PyMT mouse. g MDA-MB-231-Luc-D3H2LNc cells were infected with lentiviruses carrying shSCR, shSCR+HIF-1α, shPRAK, shPRAK+HIF-1α, or shPRAK+ HIF-1αΔTAD. The invasive capacity of these cells was analyzed using Matrigel assay. The experiments were repeated three times. Representative images and quantification of fold of invasion are shown. Error bars represent s.d. Scale bars, 100 µm. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ns, not significant. h The MDA-MB-231-Luc-D3H2LN cells described above were tested for the formation of lung metastasis following intravenous injection. Bioluminescence was recorded on day 21. Each group contained 5–7 mice. Representative images and relative photon flux are shown. Error bars represent s.d. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ns, no significant. p-value was determined by a two-tailed, unpaired t-test.