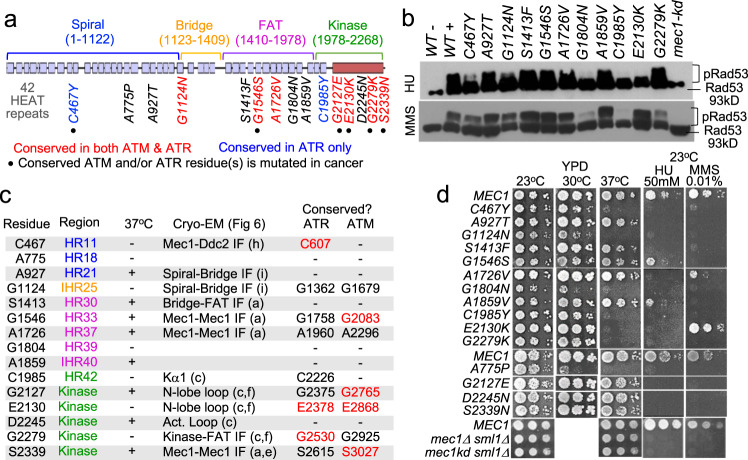
Fig. 5. An unbiased genetic screen identifies conserved Mec1 residues required for the DDR.
a Mec1 comprises 42 HEAT repeats and a kinase domain45. An unbiased genetic screen identified 15 residues critical for mediating resistance to HU and/or MMS (Supplementary Fig. 5a, Supplementary Table 2, and Supplementary Data 5). Red: residue is conserved in both ATM and ATR. Blue: conserved in only ATR. • The conserved ATM and/or ATR residue is mutated in cancer (c; Supplementary Data 3, 4, and 6; http://cbioportal.org). b Impact of the indicated mec1 allele on HU- and MMS-dependent Rad53 activation. Western blot analysis was performed using a Rad53 antibody that detects both unphosphorylated and phosphorylated species (EL7.E1)35. “WT−”: untreated negative control sample. “WT+”: positive control sample. “mec1-kd”: a kinase dead mutant in a sml1Δ suppressor mutation background used as a control. Locations of the unphosphorylated (93kD) and phosphorylated Rad53 species are indicated (Supplementary Fig. 5d). c Summary of the results presented in b and d, Fig. 6 and Supplementary Fig. 5c. Region: the colors correspond to the four domains in a. HR HEAT Repeat unit. IHR Inter-HR; the loop region following the indicated HR unit. 37 °C: growth at 37 °C (d). Cryo-EM (Fig. 6): location of the indicated residue in the Mec1–Ddc2 enzyme complex. The letters in the parenthesis corresponds to the relevant panel in Fig. 6. IF interface. Conserved?: the ATR/ATM residue corresponding to the indicated Mec1 residue (Supplementary Data 6). -: not conserved. Residues written in red are mutated in cancer (Supplementary Data 3, 4, and 6; http://cbioportal.org). d Impact of temperature, HU, and MMS on the indicated mec1 strains (“Methods”). The mec1Δ and mec1-kd control strains are in a sml1Δ suppressor mutation background necessary to maintain viability; all other mec1 mutants are in a SML1 background.