Fig. 7. Dynamic asymmetry between the cytosolic and luminal side of MGST2 coupled to solvent accessibility and one-third of the sites reactivity.
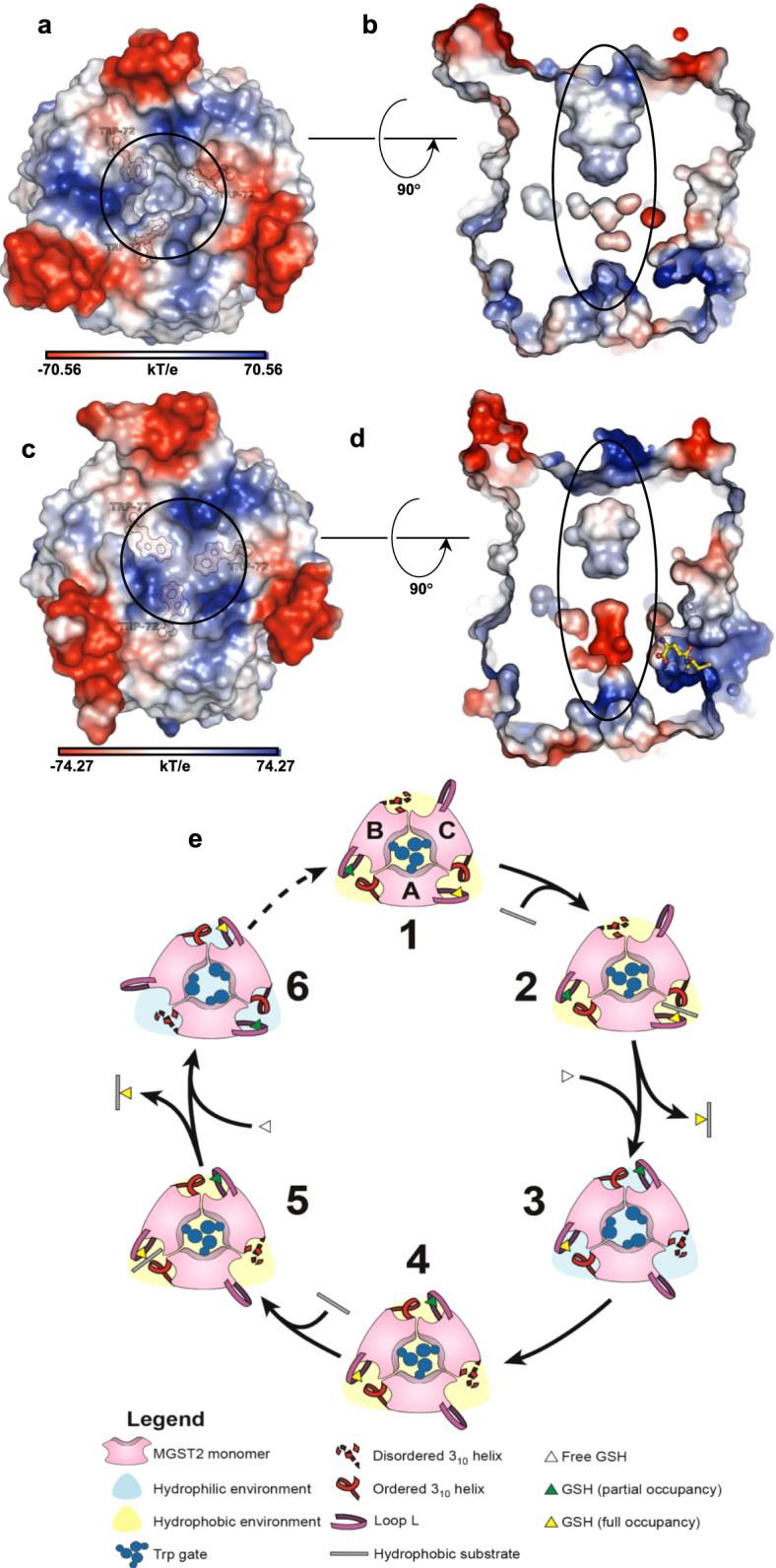
a, c Electrostatic surface representation of apo- and holo-MGST2 structures showing the opened and closed Trp-gate, (black circled region), respectively. b, d Sliced through representation of a, c, respectively, along the membrane plane showing the central solvent accessible channel in black ellipsoid. e Proposed scheme of one-third of the sites reactivity. Cytoplasmic view of holo-MGST2 with three monomers represented as A, B, and C. (1) shows the AC site with activated GSH, AB site with partially bound GSH, and BC site empty. In AC and AB sites, the 310 helical motif is ordered (helix conformation) and loop L at the cytosolic side is closed as a lid, while the BC site has disordered 310 helical motif (loop conformation) and open loop L lid. The closed Trp-gate at the luminal side restricts solvent access and creates a hydrophobic environment, which promotes the entry of hydrophobic second substrate and conjugation at the AC site (2). Next the 310 helix unfolds and loop L lid and the Trp-gate open to create a hydrophilic environment and facilitates the product release at the AC site. Simultaneously, the GSH is activated at the AB site and new GSH is partially bound at the BC site where the 310 helical motif is now in a helical conformation and loop L lid closed (3). Finally the Trp-gate closes again (4) and the next cycle of conjugation begins at the AB site (5, 6) as described in 1–4.
