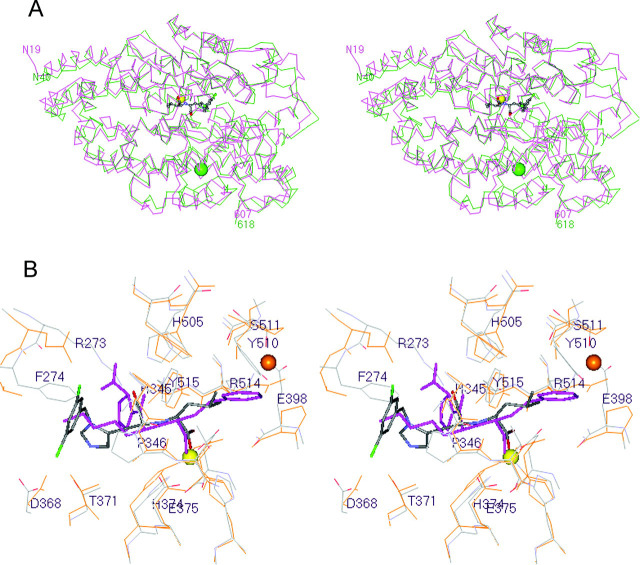
Fig. 6.
Superposition of the ACE2 and tACE structures.A, the α-carbon atoms in lisinopril-bound tACE (13) were superimposed onto the equivalent atoms in inhibitor-bound ACE2 (588 residues) with an r.m.s. deviation of 1.80 Å. MLN-4760-bound ACE2 is magenta, and lisinopril-bound tACE is green. MLN-4760 is shown bound to ACE2 with the same color code described in the legend to Fig. 4A. Similarly, the zinc and chloride ions are shown as described in the legend to Fig. 3. The orientation is the same as that shown for native ACE2 in Fig. 3. Structures were superimposed using MOE 2003.02 software. B, the 21 α-carbon atoms at the inhibitor-bound active site of ACE2 (residues 4.5 Å from the inhibitor) were superimposed onto the equivalent atoms of lisinopril-bound tACE (Protein Data Bank code 1O86) with an r.m.s. deviation of 0.53 Å. The active site of ACE2 and MLN-4760 are shown in default colors, with the inhibitor displayed in stick rendering. Labels are for ACE2 residues only. The active site residues of tACE are shown in orange, with the inhibitor lisinopril colored purple in stick rendering. The zinc ion is shown as a yellow sphere, and the second chloride ion of tACE (CL2) is shown as an orange sphere. This chloride ion site does not exist in ACE2 due to the Glu398 substitution for Pro407 (see “Results and Discussion”). Other important differences between ACE2 and tACE are as follows: Arg273versus Gln281, Phe274versus Thr282, and Tyr510versus Val518, respectively.