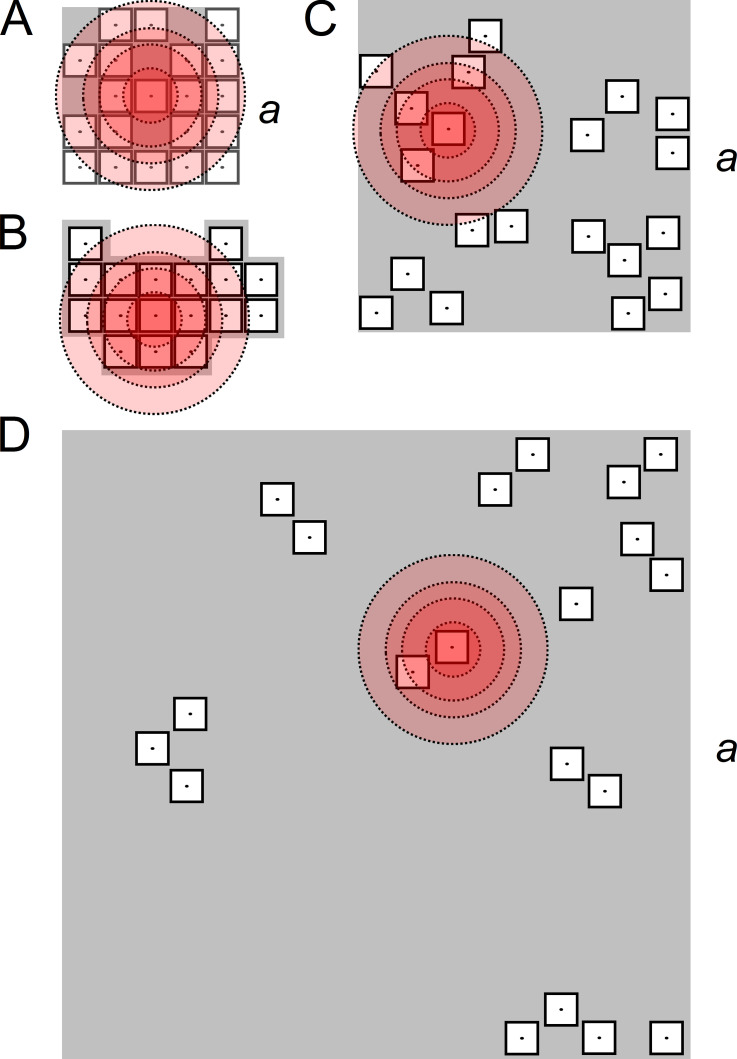
Figure 2.
Example geometric models of CRSs of different density types. (A) A compact square CRS with 20 RYRs arranged side by side on a 5 × 5 lattice; a = 150 nm. (B) A compact contact network CRS with 17 RYRs arranged side by side according to Walker et al., 2015. (C) A narrow CRS with 20 RYRs distributed according to pattern B (Table 1); a = 264 nm. (D) A wide CRS with 20 RYRs distributed according to pattern B (Table 1); a = 501 nm. The shadowed areas represent the planes of the CRSs. The empty squares with dots represent RYRs with a central ion channel, the point source of Ca2+ flux. The concentric circles of increasing diameter depict 2 µM [Ca2+] levels calculated for iCa of 0.04, 0.15, 0.25, and 0.4 pA, at which the steady-state open probability of a RYR would be 2% (see Fig. 1).