FIGURE 3.
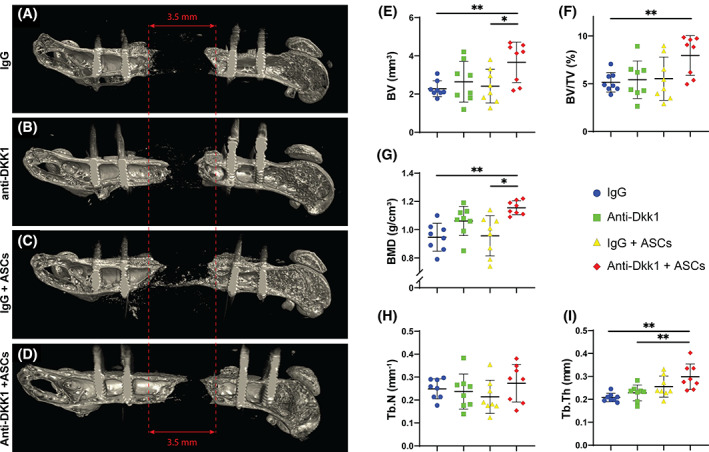
Anti‐DKK1 treatment incites ASC‐mediated bone formation as assessed by microcomputed tomography (μCT). Defects were treated with ASC seeded scaffolds or acellular control scaffolds. Animals were treated with anti‐DKK1 or IgG control (15 mg/kg, SC, twice weekly). A‐D, Representative three‐dimensional (3D) μCT reconstructions of the femoral segmental defect site at 8 weeks postoperative, shown from a sagittal perspective. Original defect size indicated by red lines. E‐I, Quantitative μCT analysis of the femoral segmental defect site, including (E) bone volume (BV), (F) fractional bone volume (BV/TV), (G) bone mineral density (BMD), (H) trabecular number (Tb.N), and (I) trabecular thickness (Tb.Th). Dots in scatterplots represent an individual animal, while crosshairs and whiskers represent mean and 1 SD, respectively. See Table S3 for a further summary of animal allocation, treatment regimens, and total cell numbers. *P < .05; **P < .01. ASCs, adipose‐derived stem cells
