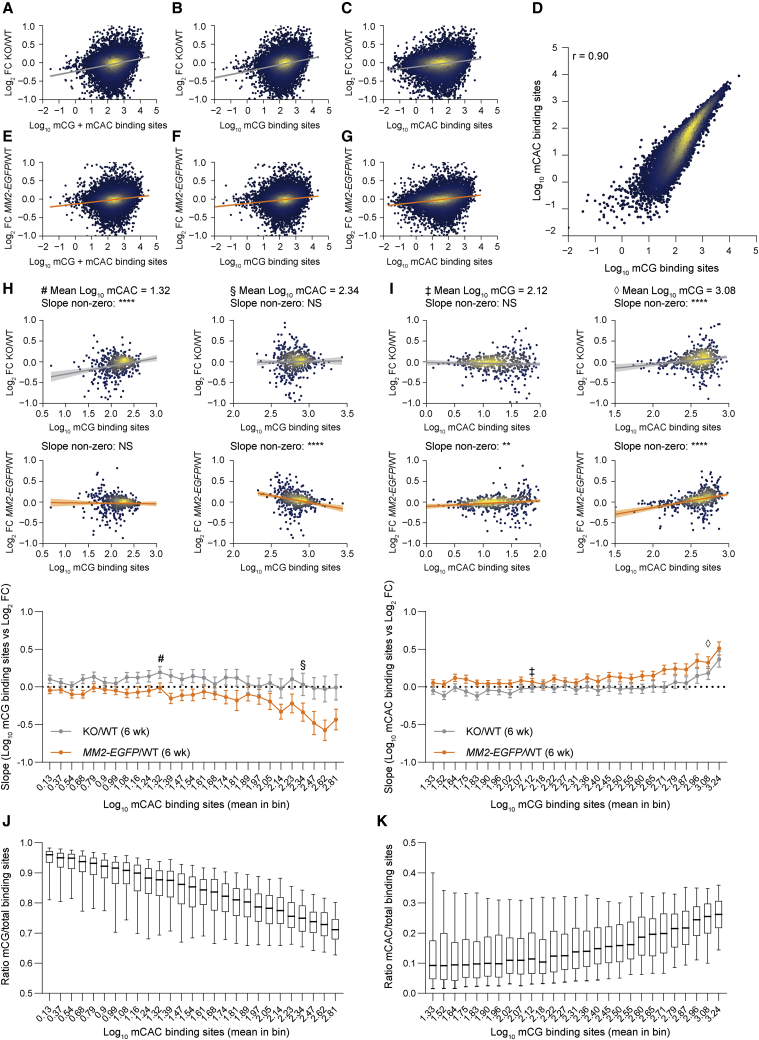
Figure 6.
MM2 represses transcription at mCG but not mCAC sites
(A–C and E–G) Correlations between the total number of MeCP2 binding sites per gene (between TSS and TTS): mCG + mCAC, mCG, and mCAC and transcriptional changes in KO/WT (A–C) and MM2-EGFP/WT (E–G) hypothalamus tissue at 6 weeks of age.
(D) Correlation between mCG and mCAC binding sites per gene in the hypothalamus at 6 weeks. Regression (r) = 0.90.
(E–G) Correlations between MeCP2 binding sites and transcriptional changes in MM2-EGFP/WT.
(H) Genes were binned by the number of mCAC binding sites to determine the effect of mCG on transcription in KO/WT and MM2-EGFP/WT (6 weeks). Two example bins are shown (# bin 12, mean log10 mCAC = 1.32; and § bin 25, mean log10 mCAC = 2.34). The slopes (±95% confidence interval) of all of the bins are shown below. See Table S1.
(I) Genes were binned by the number of mCG binding sites to determine the effect of mCAC on transcription. Two example bins are shown (‡ bin 11, mean log10 mCG = 2.12; and ‡ bin 27, mean log10 mCAC = 3.08). The slopes (±95% confidence interval) of all of the bins are shown below. See Table S2.
(J) The ratio of mCG/total binding sites per gene in each mCAC bin.
(K) The ratio of mCAC/total binding sites per gene in each mCG bin. Whiskers show 5th–95th percentiles.