Figure 2.
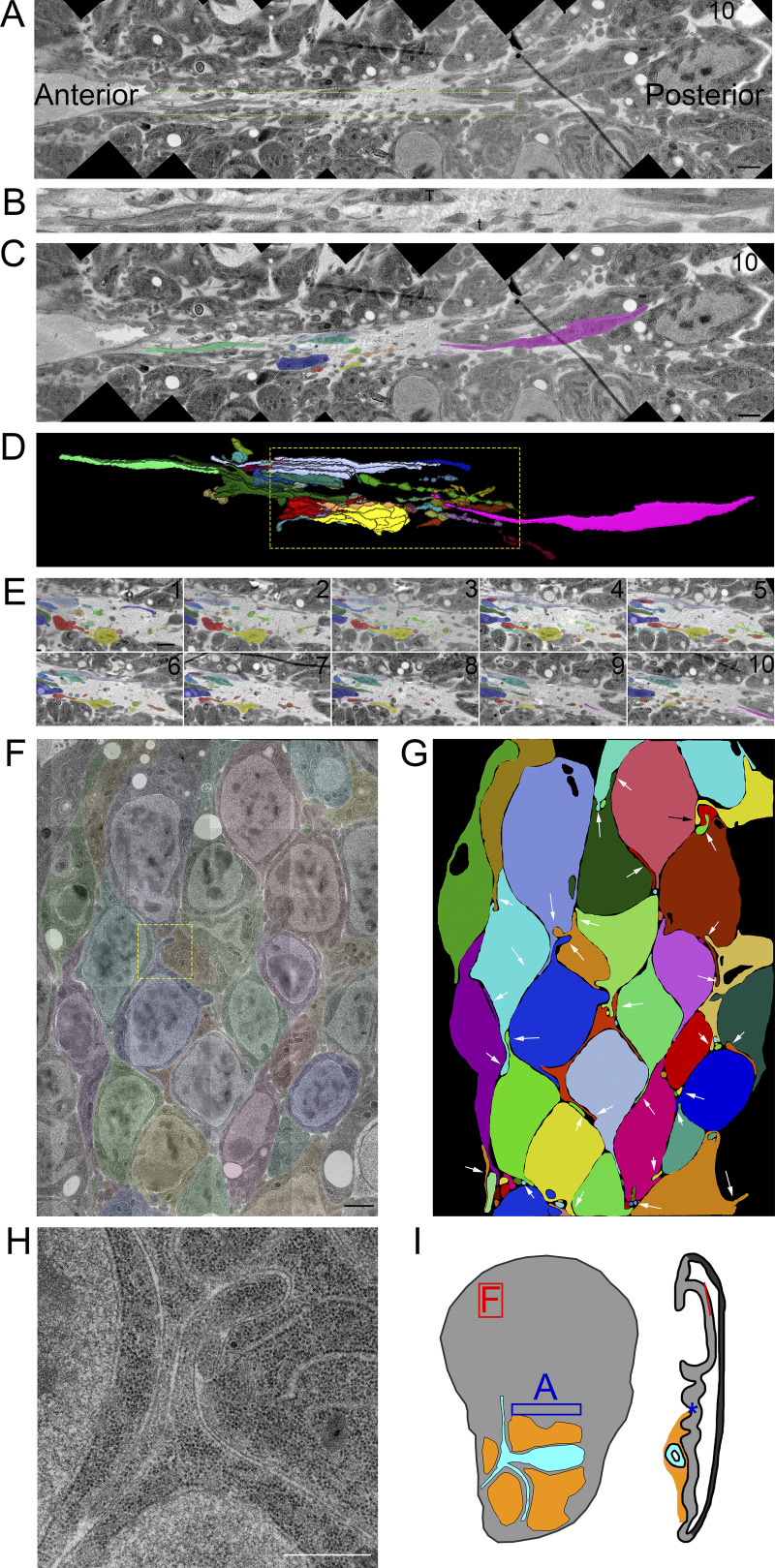
Filopodia extend from basal and lateral surfaces of disc cells. (A) One montaged image (see Materials and Methods) of a 10-section TEM series showing the basal side of the disc in a fold region (asterisk on disc diagram in Fig. 2 I). Thick membrane extensions and thin filopodia extend along the fold. (B) An enlargement of the dashed green box in A with a mix of thick membrane extensions and thin filopodia with constrictions and varicosities. (C) Segmentation of individual membrane extensions and filopodia. The section number is labeled in the top-right corner. (D) 3D reconstruction of segmentation showing thick membrane extensions, thin filopodia, and a thick membrane extension that narrows to a filopodia (pink). The reconstructed volume containing the extensions is 21.6 × 2.7 × 0.7 µm. (E) Each of the 10 segmented sections used to produce the boxed region of D. (F) One section of an eight-section TEM series of the wing pouch, which shows filopodia extending from the lateral surfaces of disc cells. The montage of original images has been overlayed with transparent segmentation of individual cells. (G) Segmentation of the cells shown in F with arrows pointing to the lateral filopodia. (H) Enlargement of the yellow boxed area in panel F shown without transparent segmentation. (I) Disc diagram representing the areas imaged and shown in A (blue box and asterisk) and F (red box and line). Scale bars: 1 µm (A, C, and F) and 500 nm (H).