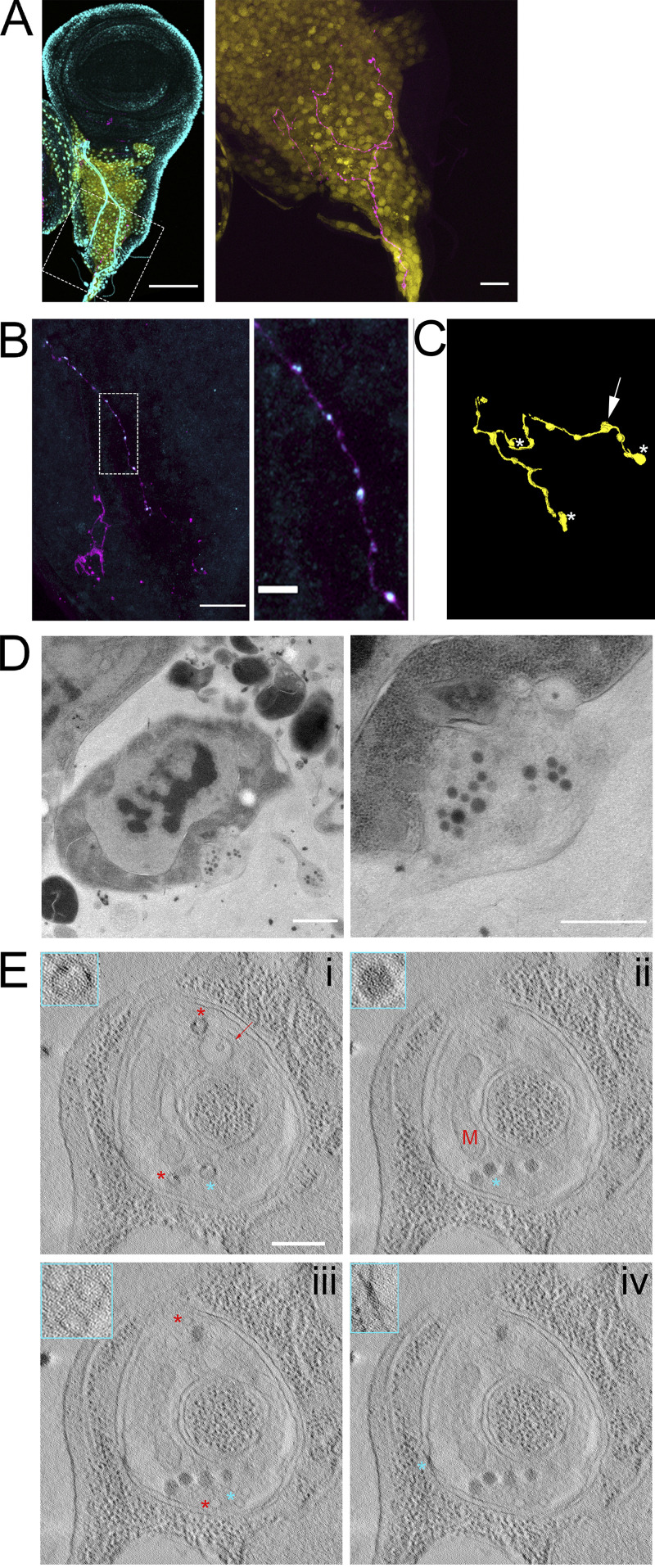
Figure 9.
Synaptic vesicles are preserved in a neuron synapsing with wing disc myoblasts. (A) A fixed wing and leg disc from an L3 larva expressing GFP (yellow) under the control of 1151-Gal4 labeled with DAPI (cyan) and HRP-Alexa Fluor 647. The neuron (magenta) can be seen among the myoblast layer (yellow) of the wing disc. The right panel is shown without DAPI signal. (B) A portion of a fixed disc stained for HRP (magenta) and synaptotagmin (cyan). Confocal images are shown as Z projections. (C) A portion of the myoblast region was imaged by TEM in 40 serial 100-nm sections. The montaged and aligned images were used to segment and 3D reconstruct the neuron. The location of four identified synapses along the neuron are indicated by an arrow, corresponding to the synapse shown in D, or by asterisks. (D) A TEM image showing a section of one of the observed neuron–myoblast synapses. At higher magnification (right), vesicles are apparent. (E) Images from a tomographic tilt series containing the synapse shown in D. Tomography revealed vesicles with electron-dense cargo appearing as puncta on the inner edge of vesicles (i, asterisks), a membranous compartment containing a smaller vesicle (i, arrow), a mitochondrion (ii, M), dense core vesicles (ii, asterisk), clear synaptic vesicles (iii), and electron-dense junctions (iv) between the neuron and myoblast membranes. The insets outlined in cyan show enlarged portions of the image that correspond to cyan asterisks, while red asterisks indicate other examples of the feature shown in the inset. Scale bars: 100 µm (A, left), 20 µm (A, right, and B, right), 1 µm (D, left), and 500 nm (D, right, and E).