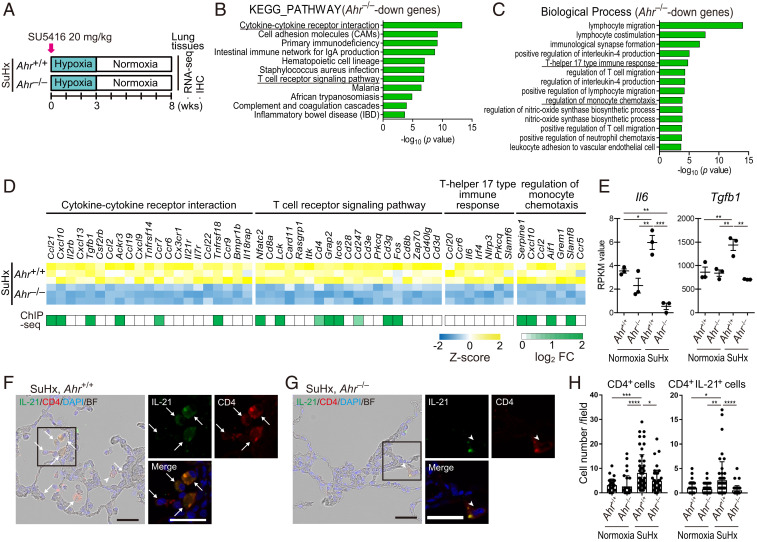
Fig. 7.
AHR induces up-regulation of inflammatory signals and accumulation of CD4+IL-21+ T cells in vascular lesions in the advanced stage of SuHx rats. (A) Experimental protocol for RNA-seq (n = 3 for each group) and ChIP-seq (n = 3 pooled samples for each group) in the advanced stage of SuHx rats. SU5416 was subcutaneously administered to Ahr+/+ and Ahr−/− rats once on day 0. (B) KEGG pathway enrichment analysis of 702 Ahr−/−-down genes identified by RNA-seq analysis in SuHx rat lung at 8 wk. (C) GO enrichment analysis of the 702 genes. (D) Z-score of RNA-seq data and log2 fold change of enriched genes of ChIP-seq data about cytokine–cytokine receptor interaction, T cell receptor signaling pathway, T helper 17 type immune response, and regulation of monocyte chemotaxis in B and C. (E) RPKM values calculated in RNA-seq of representative genes about T helper 17 type immune response, Il6 and Tgfb1. (F) Representative immunohistofluorescence images of pulmonary arterioles of SuHx 8-wk Ahr+/+ rats stained for IL-21 and CD4. Arrows indicate cells double-positive for IL-21 and CD4 (CD4+IL-21+). Arrowheads indicate CD4+ cells with attenuated expression of IL-21. (Scale bar, 30 μm.) (G) Representative immunohistofluorescence images of pulmonary arteries of SuHx 8-wk Ahr−/− rats stained with IL-21 and CD4. (H) Number of CD4+ cells and CD4+IL-21+ cells of SuHx 8-wk Ahr+/+ and Ahr−/− rats in 724 mm × 541 mm fields captured around arteries (number of tested rats: normoxia Ahr+/+: n = 3, normoxia Ahr−/−: n = 3, SuHx 8-wk Ahr+/+: n = 5, SuHx 8-wk Ahr−/−: n = 4). Values are means ± SD; ****P < 0.0001, **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05.