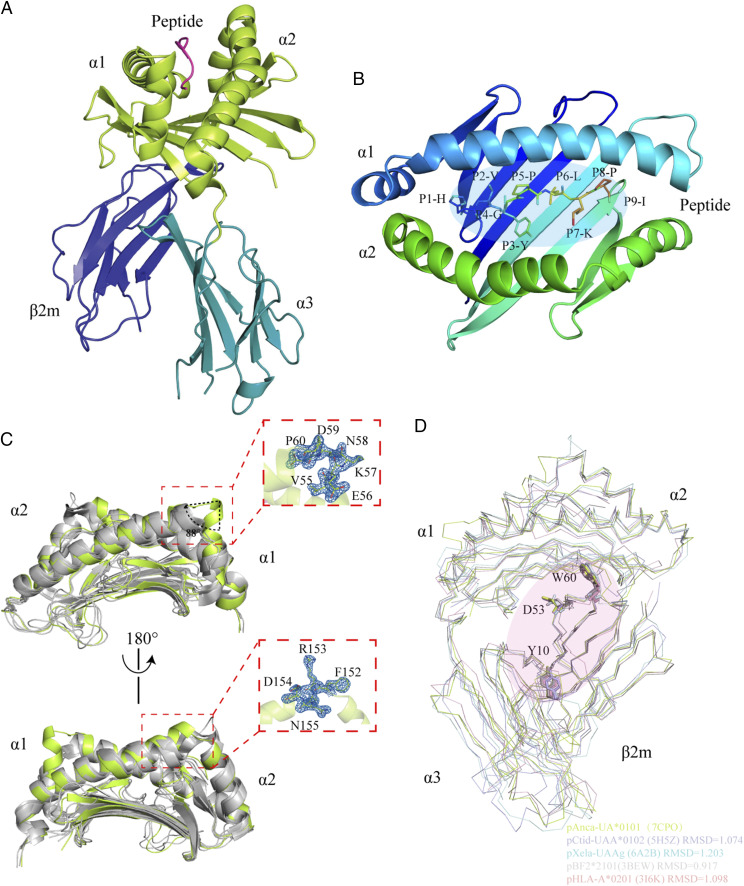
FIGURE 1.
Structural overview of the green anole pAnca-UA*0101 complex. (A) The HC of pAnca-UA*0101 consists of three domains including α1 and α2 shown in lime green and α3 shown in teal. β2m is shown in deep blue. The peptide HVYGPLKPI is shown in magenta. (B) The binding of the HVYGPLKPI peptide in the PBG of pAnca-UA*0101. (C) Special features of the pAnca-UA*0101 PBG. Structural comparison of the α1 and α2 domains of pAnca-UA*0101, bony fish MHC-I (pCtid-UAA*0102, PDB ID: 5H5Z), African frog MHC-I (pXela-UAAg, PDB ID: 6A2B), chicken MHC-I (BF2*2101, PDB ID: 3BEW), and human MHC-I (HLA-A*0201, PDB ID: 3I6K). Except for pAnca-UA*0101 shown in lime green, other MHC-Is are shown in gray to better identify special sites. The features were identified in the α1 and α2 domains. The α-helix adjacent to the C terminus of the α1 domain forms an ∼88° flip absent in other MHC-I molecules. Additionally, 152F-155N in the α2 domain induce a significant upward shift. The map of these structurally differential amino acids is shown on the right. (D) Conserved amino acids involved in the interaction between Anca-UA*0101 and Anca-β2m. Amino acids involved in the interaction of HC with L chain (LC) include Y10, D55, and W60 of β2m that are conserved in human, chicken, green anole, frog, and grass carp. The RMSD values are labeled.