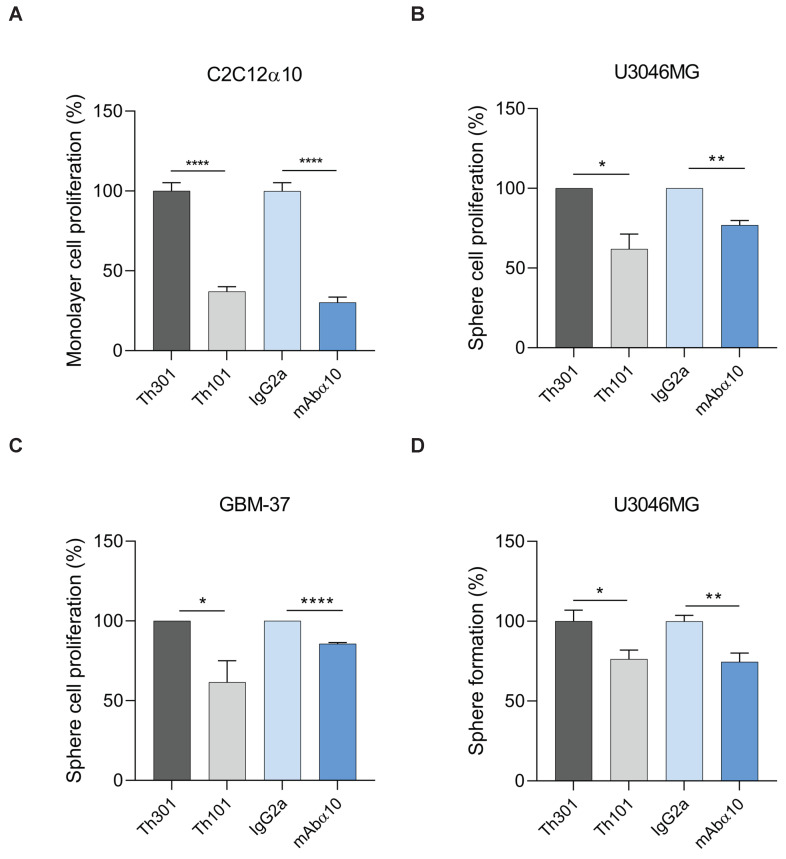
Figure 5.
Integrin α10 antibodies inhibit GB cell proliferation and sphere formation (A) C2C12α10 cells were seeded in 96-well plates pre-coated with 20 µg/mL of collagen I (Col I). Cells were treated with Th101, mAbα10 antibodies or their isotype controls Th301 or IgG2a at 10 µg/mL concentration. After 24 h of incubation with the different antibodies, BrdU was added for incorporation into dividing cells during DNA synthesis and to detect proliferation. C2C12α10 cell proliferation was decreased in the presence of both human and mouse integrin α10 antibodies, but not by the control antibodies. (B,C) U3046MG and GBM-37 glioblastoma cells were seeded as sphere cultures and treated with 10 µg/mL of Th101, mAbα10, or control antibodies for 8 days. Twenty-four hours before harvest, BrdU was added. Cells were stained with APC-conjugated anti-BrdU antibody to measure the amount of BrdU incorporated in the replicating cells. The mean fluorescence intensity of BrdU was determined by flow cytometry and is shown as BrdU intensity of anti-integrin α10-treated cells normalized to its isotype control. (D) U3046MG cells were grown as spheres in the presence or absence of 10 µg/mL of Th101, mAbα10, Th301, or IgG2a. The number of spheres was analyzed on day 8 (mean ± SE). The number of spheres per field of microscope view in each experimental group was quantified by Fiji software and statistical analysis of the average diameter of spheres. All results were from at least three independent experiments with triplicates in each experiment and expressed as mean ± SE. Unpaired two-tailed Student t-test was applied. Four levels of significance were used for a 95% confidence interval, where * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; and **** p < 0.0001.