Figure 2. Sources of cis-regulatory variation in eukaryotes.
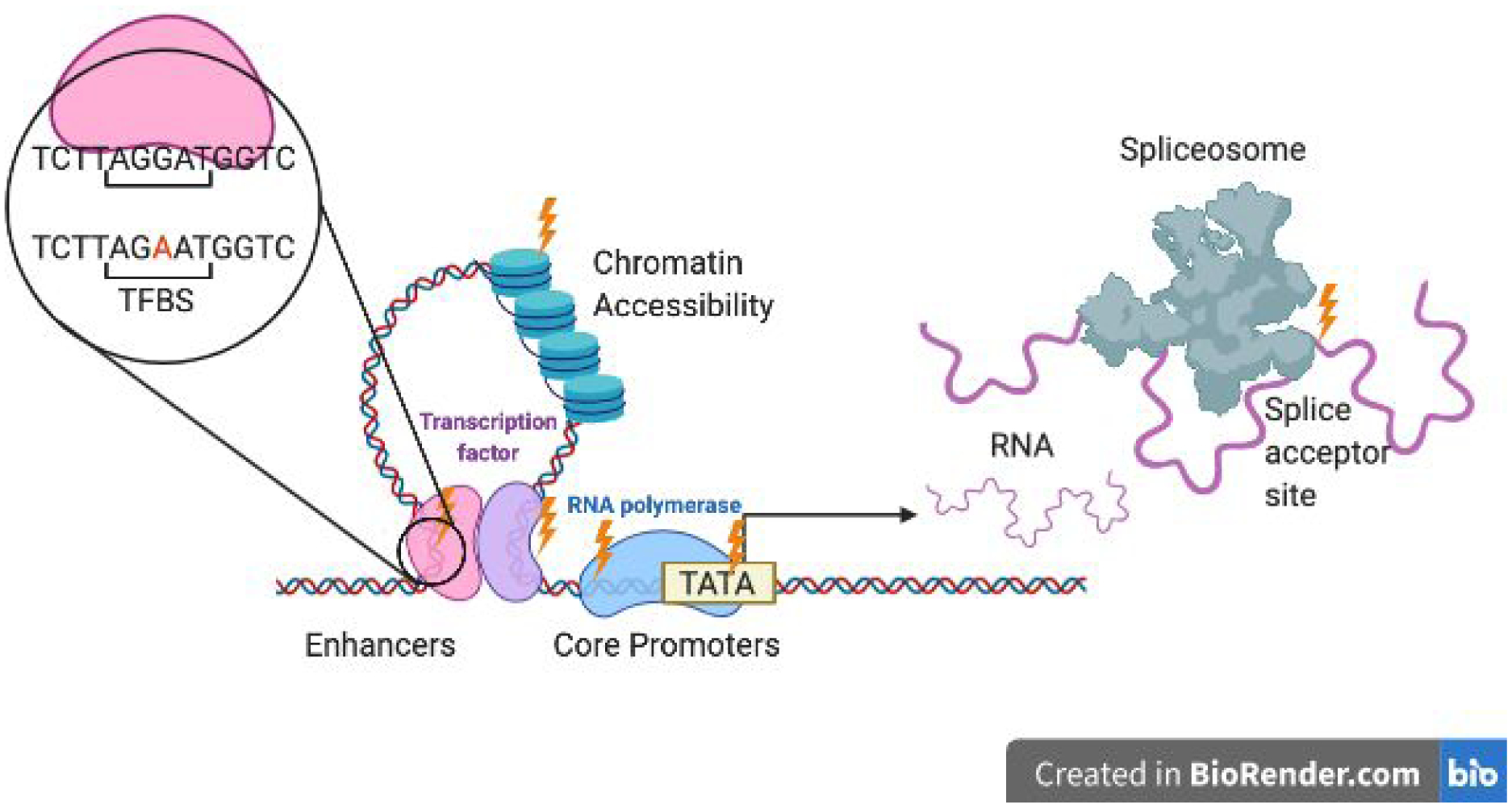
Mutations (indicated with lightning bolts) affecting the core promoter (including in motifs such as the TATA box used to assemble the transcription machinery activating RNA polymerase), enhancers (whose functional units are transcription factor binding sites (TFBS)), chromatin accessibility (altered by nucleosome placement and stability) can have cis-regulatory effects on gene expression. Mutations that affect the splicing, stability, and/or translation of mRNA in an allele-specific manner can also be sources of cis-regulatory variation.
