Fig.7.
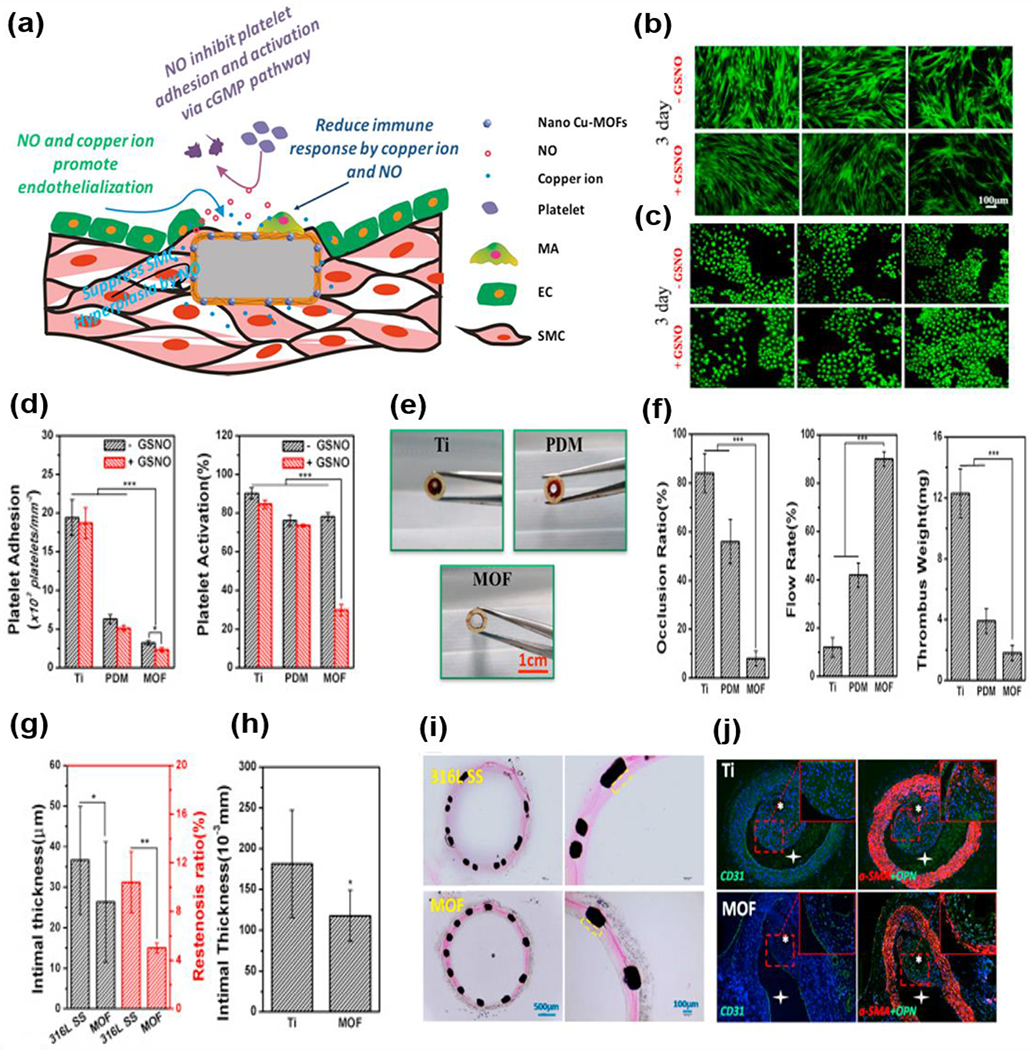
(a) Schematic of nano Cu-MOFs-immobilized coating function. The NO release and copper ion delivery of the nano Cu-MOFs-immobilized coating exhibited a synergistic effect on inhibiting platelet adhesion and activation, promoting endothelialization, regulating immune response, and suppressing SMCs hyperplasia. (b-c) Rhodamine staining of ECs (b) and SMCs (c) on samples for 3 days. (d) Platelet adhesion and activation level after 45 min incubation with or without a NO donor. (e) Cross-sectional observation of the sample containing catheters after 30 min circulation. (f) Occlusion ratio of a sample containing catheters by measuring the cross-section diameter of the circulating tube. (g) Statistical analysis of the neointimal thickness and restenosis rate. (h) Intimal thickness of Ti and nano Cu-MOFs-immobilized Ti wire after implantation into the abdominal aorta of rats for four weeks. (i) Effect of the bare stents and nano Cu-MOFs-immobilized stents on in-stent restenosis assessed by histomorphometric analysis. (j) Immunofluorescence staining of the abdominal aorta after implantation for four weeks for CD31 (green), α-SMA (red), OPN (osteopontin) (green). Reproduced with permission from Ref. [232]. Copyright 2019, Elsevier.
