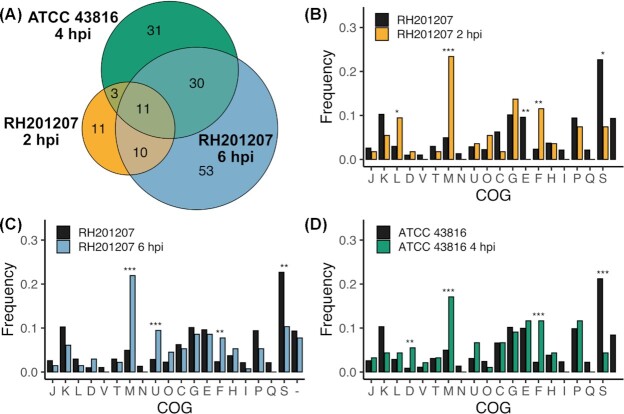
Figure 4.
Multiple genes, including the cps cluster contribute to the fitness during Galleria infections of both classical and hypervirulent K. pneumoniae. (A), Venn diagram showing the overlap of significantly less abundant insertion mutants in the classical ST258 strain RH201207 and the hypervirulent strain ATCC 43816. Only non-essential genes shared by both strains as determined by a bi-directional best blast analysis are shown. (B–D), Cluster of orthologous groups (COG) enrichment analysis shows an overrepresentation of outer membrane biogenesis as well as nucleotide transport and metabolism genes in all sets of significantly depleted genes during G. mellonella infection. Genes were assigned to Cluster of Orthologous Groups (COG) (Tatusov et al. 2000) with eggNOG. The bars represent the percentage of genes that belong in that category. Black bars denote the frequency of COGs in all non-essential genes of the particular strain, the frequency of all significantly depleted genes after Galleria infection is coloured as follows, A: RH201207 2 hpi, B: RH201207 6 hpi, C ATCC 43816 4 hpi. P-values were determined by Fisher's exact test in R and the level of significance is indicated by asterisks (*, P <0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001). COGs without genes assigned to them (A, B, R, W, Y & Z) were removed. Abbreviations of COGs: J, Translation, ribosomal structure and biogenesis; K, Transcription; L, Replication, recombination and repair; D, Cell cycle control, cell division, chromosome partitioning; V, Defence mechanisms; T, Signal transduction mechanisms; M, Cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis; N, Cell motility; U, Intracellular trafficking, secretion, and vesicular transport; O, Post-translational modification, protein turnover, chaperones; C, Energy production and conversion; G, Carbohydrate transport and metabolism; E, Amino acid transport and metabolism; F, Nucleotide transport and metabolism; H, Coenzyme transport and metabolism; I, Lipid transport and metabolism; P, Inorganic ion transport and metabolism; Q, Secondary metabolites biosynthesis, transport and catabolism; S, Function unknown; -, no hit.