Fig. 4. The effects of knockout of TRB3 on high-fat diet-induced BAT impairment.
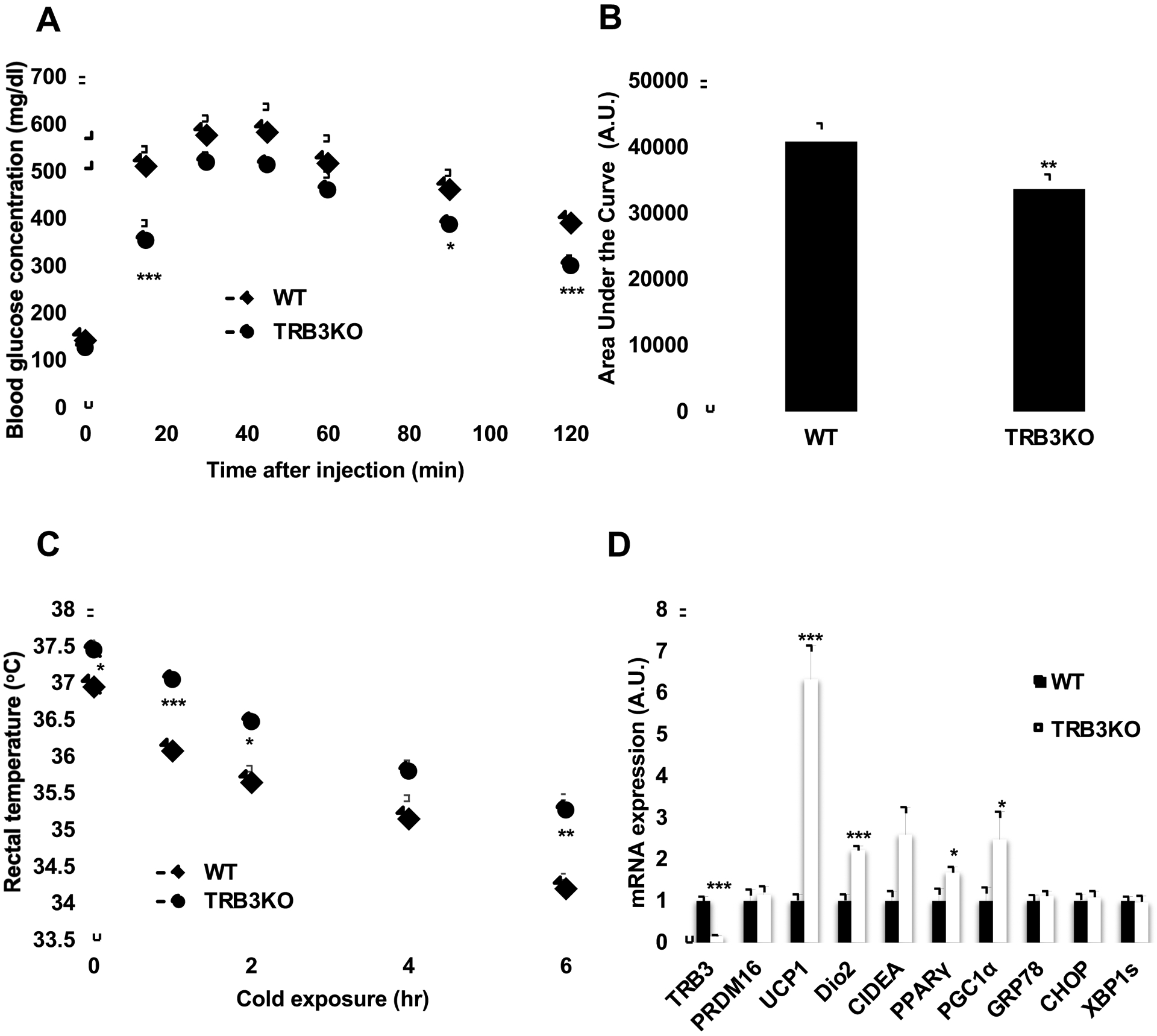
(a-d) Wild type (WT) and TRB3KO mice at 6 weeks of age were placed on a high-fat diet for 16 weeks (n=5). (a,b) At 12 weeks of high-fat diet, mice were fasted for 14 h to perform a glucose tolerance test. TRB3KO mice had improved glucose tolerance (a) and lower area under the curve during the glucose tolerance test (b). (c) At 16 weeks of high-fat diet, mice were placed at 4°C for 6 h. Core temperature was measured at indicated times. (d) mRNA from brown adipose tissue was collected and used to determine mRNA expression for multiple genes. Data are the means ± S.E.M. * indicates p<0.05, ** indicates p<0.01, and *** indicates p<0.001 vs. WT.
