FIGURE 2.
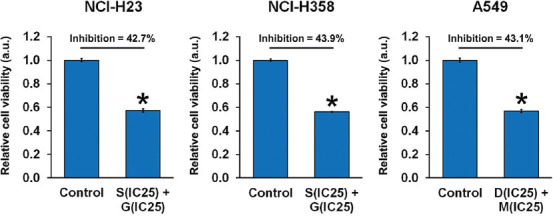
Combined effect of activated CDC42-associated kinase 1 (ACK1) and protein kinase B (AKT) inhibition on non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cell viability. NSCLC cell lines NCI-H23, NCI-H358, and A549 were treated with combinations of an ACK1 inhibitor (dasatinib, D; sunitinib, S) and an AKT inhibitor (MK-2206, M; GDC-0068, G) at the calculated optimal concentrations. Cell viability was evaluated using MTT assay after 48 hours of culture with each drug combination. For NCI-H23 and NCI-H358 cells, sunitinib at IC25 (2.03 μM and 1.98 μM, respectively) combined with GDC-0068 at IC25 (1.08 μM and 0.80 μM, respectively) significantly suppressed cell viability by 42.7% and 43.9%, respectively, after 48 h of treatment. For A549 cells, dasatinib at IC25 (3.88 μM) combined with MK-2206 at IC25 (0.99 μM) significantly suppressed cell viability by 43.1% after 48 h of treatment. The results are shown as the mean ± SD (n = 3, t-test), *p < 0.05 vs. control. IC25 represents the quarter maximal inhibitory concentration; a.u.: arbitrary units.
