FIGURE 3.
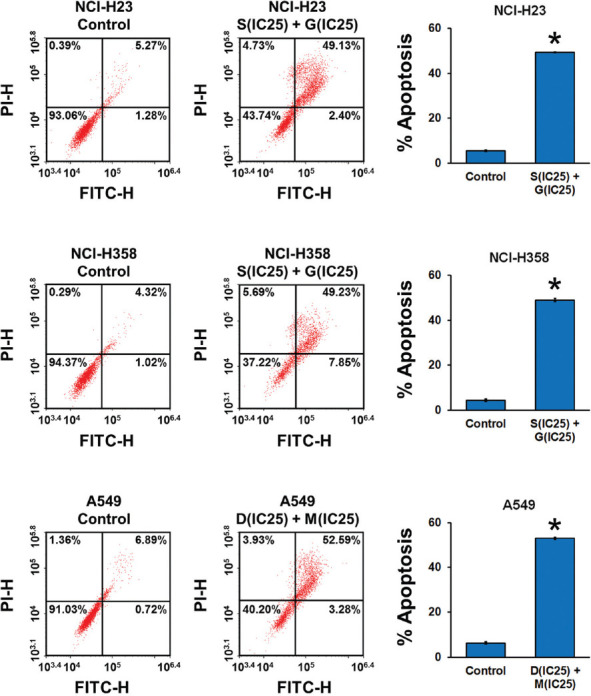
Combined effect of activated CDC42-associated kinase 1 (ACK1) and protein kinase B (AKT) inhibition on non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cell apoptosis. NSCLC cell lines NCI-H23, NCI-H358, and A549 were treated with combinations of an ACK1 inhibitor (dasatinib, D; sunitinib, S) and an AKT inhibitor (MK-2206, M; GDC-0068, G) at the calculated optimal concentrations. Cell apoptosis was evaluated using flow cytometry after 24 hours of culture with each drug combination. Bar graphs illustrate the percentage of late apoptotic cells (the upper right quadrant in the flow cytometry plot). The results of flow cytometry revealed that combined treatment with ACK1 and AKT inhibitors at optimal concentrations significantly increased the late-apoptotic population of NCI-H23, NCI-H358, and A549 cells. The results are shown as the mean ± SD (n = 3, t-test), *p < 0.05 vs. control. IC25 represents the quarter maximal inhibitory concentration; FITC: fluorescein isothiocyanate; PI: propidium iodide.
