FIGURE 5.
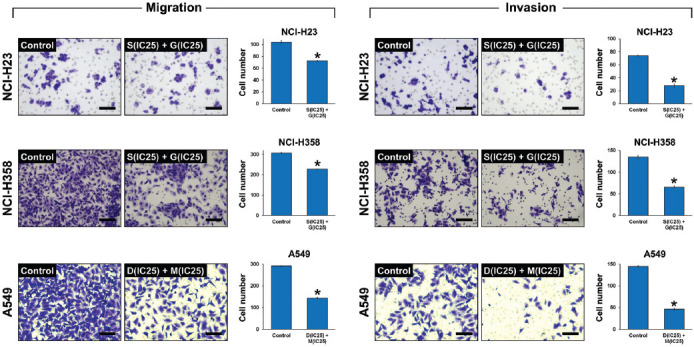
Combined effect of activated CDC42-associated kinase 1 (ACK1) and protein kinase B (AKT) inhibition on non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cell migration and invasion. NSCLC cell lines NCI-H23, NCI-H358, and A549 were treated with combinations of an ACK1 inhibitor (dasatinib, D; sunitinib, S) and an AKT inhibitor (MK-2206, M; GDC-0068, G) at the calculated optimal concentrations. Cell migration and invasion were evaluated using Transwell assay after 48 hours of culture with each drug combination. The combined treatment with ACK1 and AKT inhibitors at optimal concentrations caused significantly impaired migration of NCI-H23, NCI-H358, and A549 cells by 30.1%, 25.8%, and 50.5%, respectively, compared to that of control cells. Meanwhile, the invasion of these cells was reduced by 62.2%, 51.2%, and 68.0%, respectively. Scale bar = 100 μM. The results are shown as the mean ± SD (n = 3, t-test), *p < 0.05 vs. control. IC25 represents the quarter maximal inhibitory concentration.
