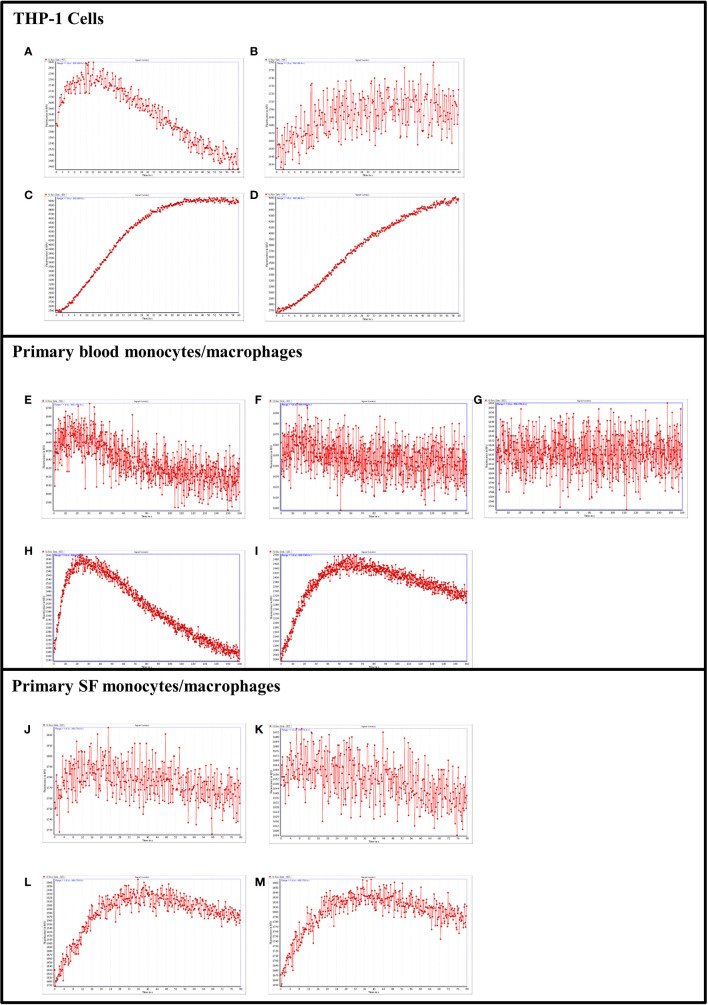
Figure 8.
PAR2 and tryptase-6 trigger calcium signals in THP-1 cells and PsA PAR2+ monocytes/macrophages. Calcium signaling assay using the fluorescent indicator, Fluo-4 AM, was used to confirm the signaling potential of PAR2 and determine whether tryptase-6 can elicit a calcium response via PAR2 in THP-1 cells and primary monocytes/macrophages from PsA patients. Stimulation with 2fLI in THP-1 (150 µM, A) or primary blood PAR2+ monocytes/macrophages (100 µM, E) was inhibited 12% (B) and 8% (F) by 1 µM of I-191, respectively. In blood cells, 2 µM of I-191 inhibited this signal by 27% (G). Stimulation of THP-1 cells (C) and primary cells (H) with volume equivalent to 44.8 or 89.6 FU/min/ng tryptase-6 isolated with the antibody affinity column from PsA SF, respectively, caused an elevation of intracellular calcium. Treatment with 1 µM of I-191 caused a 15% (D) and 13% (I) inhibition of this signal, respectively. Similarly, in primary SF monocytes/macrophages, 2fLI (200 µM, J) and volume equivalent to 44.8 FU/min/ng tryptase-6 (L) caused a calcium flux that was inhibited 51% (K) and 40% (M) by 1 µM of I-191, respectively. Calcium traces are shown with agonists (2fLI and tryptase-6) added at time zero with or without pre-treatment with I-191 (x-axis=time post addition of agonist, y-axis=units of fluorescence due to calcium release).