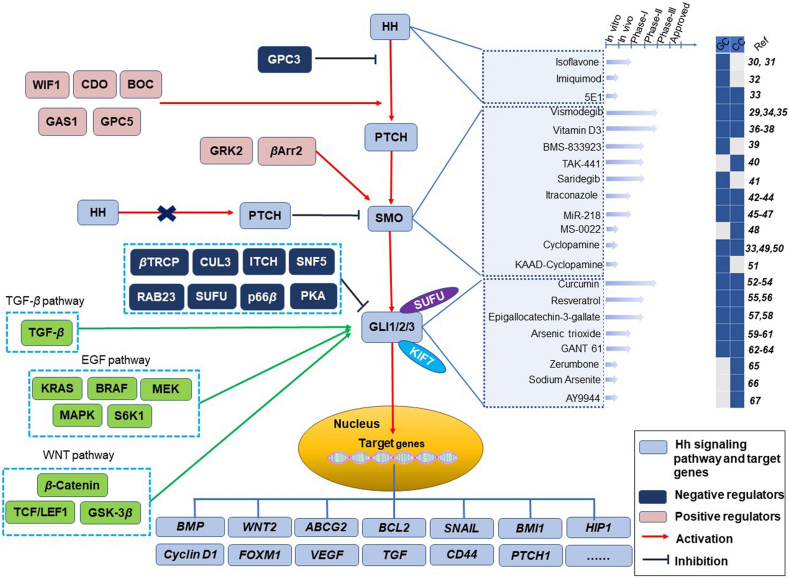
Figure 1.
The Hedgehog (HH) signaling pathway and its related regulators, target genes and current therapeutic landscape. The coreceptors for HH include cell adhesion molecule-related/downregulated by oncogenes (CDO), brother of CDO (BOC), growth arrest-specific 1 (GAS1), glypican 3 (GPC3) and glypican 5 (GPC5). Wingless/Integrated (WNT) inhibitory factor-1 (WIF1) affects HH signaling via CDO, BOC or GPC5. The function of Smoothened (SMO) needs β-arrestin 2 (βArr2) and G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 (GRK2). Suppressor of Fused (SUFU)/KIF7 is involved in the processing of glioma-associated oncogene homologue (GLI) molecules. Other negative regulators of GLI molecules include RAB23, protein kinase A (PKA), SUFU, sucrose non-fermenting 5 (SNF5), cullin-3 (CUL3), p66β, β-TRCP and Itch. Patched (PTCH) is shuttled out of the cilium and cannot inhibit SMO in the presence of HH, and HH binding promotes a conformational change in SMO. However, PTCH inhibits SMO signaling independent of HH ligand binding. The pathways interacting with the HH pathway, including the transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) pathway, epidermal growth factor (EGF) pathway and WNT pathway, are shown in green. HH inhibitors that have been effective in treating gastrointestinal tumors include isoflavone30,31, imiquimod32 and 5E133. SMO inhibitors that have been effective in treating gastrointestinal tumors include vismodegib29,34,35, vitamin D336, 37, 38, BMS-83392339, TAK-44140, saridegib41, itraconazole42, 43, 44, miR-21845, 46, 47, MS-002248, cyclopamine33,49,50 and KAAD-cyclopamine51. GLI inhibitors that have been effective in treating gastrointestinal tumors include curcumin52, 53, 54, resveratrol55,56, epigallocatechin-3-gallatel57,58, arsenic trioxide59, 60, 61, GANT 6162, 63, 64, zerumbone65, sodium arsenite66 and AY994467. Dark blue represents the type of tumor that the inhibitor is effective in. The arrows indicate progress. CC, colorectal cancer; GC, gastric cancer; BMP, bone morphogenetic protein; FOXM1, forkhead box protein M1; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; TCF/LEF1, T-cell factor/lymphoid enhancer factor1; GSK-3β, glycogen synthase kinase-3β; HIP1, Huntingtin-interacting protein 1; BMI-1, B cell-specific Moloney murine leukemia virus insertion region-1; Ref, reference.