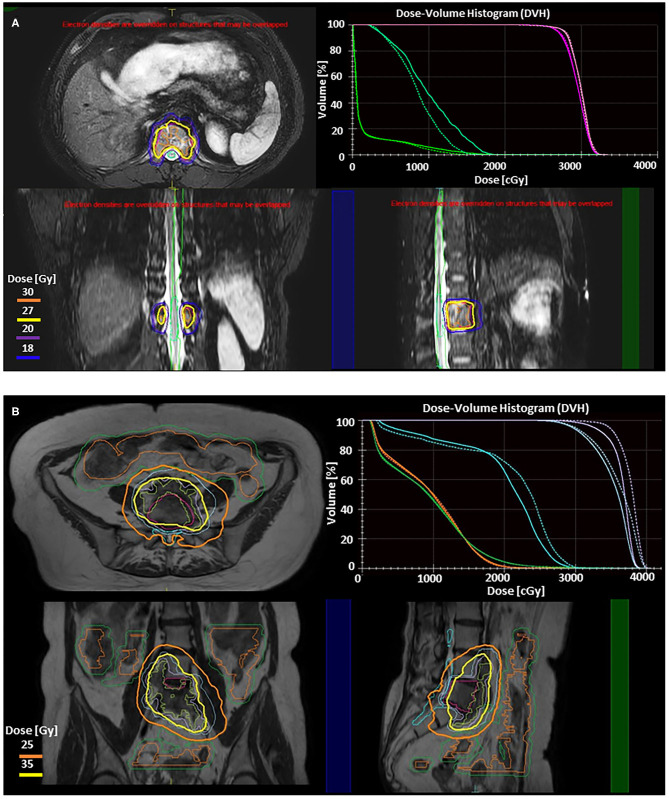
Figure 2.
Illustration of two adaptive approaches on the 1.5 T Elekta Unity (Stockholm, Sweden) MRgRT system for stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) of spine metastases. Adapt to position (ATP) is used to correct for translational shifts by adjusting beam apertures and weights without altering reference contours. Adapt to shape (ATS) accounts for all interfraction changes by re-optimizing the plan based on the MRI of the day, and requires adjustment of the target and adjacent organ at risk (OAR) contours. These treatment strategies have been described elsewhere as well as their utilization for upper abdominal SBRT (109, 110). Real-time cine MRIs acquired in perpendicular planes through the PTV center of mass are used to monitor the target during radiation delivery. (A) Axial, sagittal, and coronal slices from 3D T2 fat suppressed MR images from Unity showing ATP SBRT plan to T12 metastatic thyroid lesion (GTV Pink, PTV Magenta). Prescription was 27 Gy (yellow) in 3 fractions. 30 Gy (orange), 20 Gy (purple), and 18 Gy (blue) isodose lines are also shown. DVH in right upper panel compares the reference plan (solid lines) to the adaptive plan (dashed lines). This case involves a thoracic vertebrae metastasis without any extraosseous component. The target had good separation from dose limiting organs at risk without large variations in either target or OAR position or shape, making an ATP adaptive workflow optimal as recontouring is not necessary. For ATP, after the patient is positioned on the table daily MR images are obtained, fused with the reference plan, and shifts reviewed and approved by physician prior to beginning adaptation. During the adaptive process, mpMRI can be obtained simultaneously. Once a new plan is calculated, it can be reviewed by the physician, along with a verification MR and real-time cine MRI to confirm no significant intrafraction motion. The dose volume histogram (DVH) in the right upper panel demonstrates preserved target coverage with improved OAR doses for treatment. For conventionally fractionated treatments, total time on the table for patients range from 18 to 26 min, while this patient's SBRT delivery ranged from 40 to 60 min per treatment. (B) Axial, coronal, and sagittal slices from T2 MR images from Unity showing ATS fraction of SBRT plan to colorectal metastasis at L5 with anterior extraosseous extension. Prechemotherapy volume (blue) was prescribed 25 Gy in 5 fractions (orange) while Post-chemotherapy volume (purple) was prescribed 35 Gy in 5 fractions (yellow). DVH in right upper panel compares reference plan (solid lines) to the adaptive plan (dashed lines), demonstrating isotoxic treatment to the cauda (teal), small bowel (orange), and small bowel PRV (green) while improving coverage to both target volumes. Here the target is within close proximity to both large and small bowel. Here we use the ATS approach, with a unique parallel contouring work flow that has been described elsewhere (111). The target was rigidly fused on the daily MR, but bowel contours were different for each of five daily fractions, requiring recontouring. This allowed for maintenance of target coverage without violation of OAR constraints. ATS workflows take longer due to time required for recontouring and adapting the reference plan to not just translational shifts but new relative anatomy. For this patient the total table time ranged from 59 to 70 min.