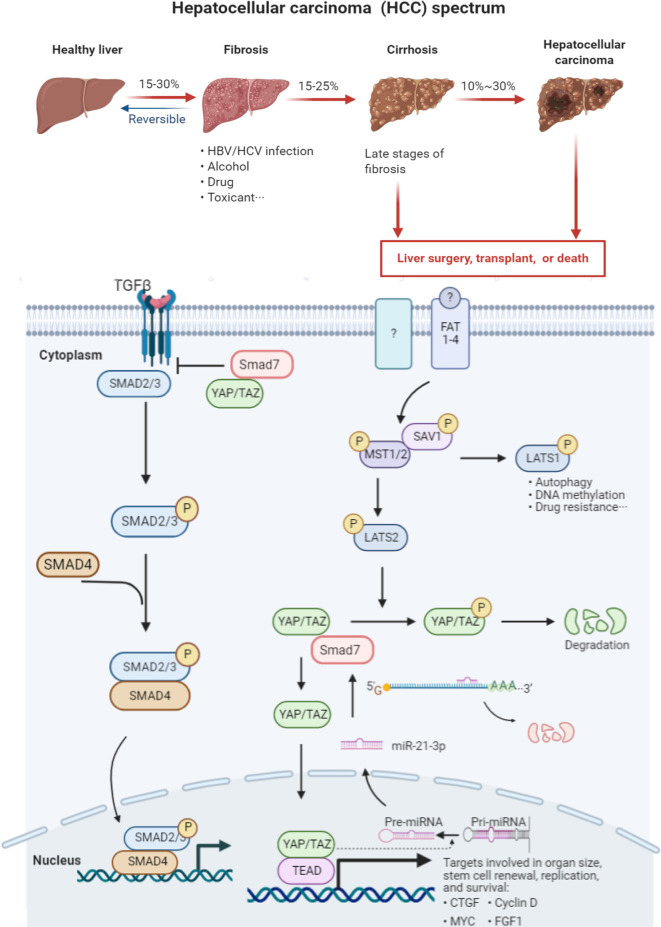
Figure 7.
Graph abstract HCC manifestation is typically preceded by hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis. There are limited cures for patients suffering advanced liver cirrhosis and HCC. Dysfunction of the Hippo signaling and TGF-beta transduction pathways plays a vital role in the pathogenesis and course of this illness. YAP1 recruits SMAD7 to activated TGF-β receptor I (TβRI), hampering the formation of co-SMAD (SMAD2/3 and SMAD2/4) complexes. These SMAD complexes are thus unable to enter the nucleus to activate transcription of downstream effectors. SMAD7 serves as the negative regulator of the TGF-β signaling pathway. The Hippo signaling pathway is composed of a series of kinases including MST1/2, LATS1/2, and nuclear effector YAP1. Once the Hippo pathway is activated, LATS1/2 is phosphorylated by MST1/2. LATS1 is mainly involved in cell autophagy, DNA methylation and drug resistance. LATS2 phosphorylates YAP1, leading to its degradation. Overexpressed miR-21-3p directly silences SMAD7 expression by binding to its 3′-UTR region, further impairing the linkage between SMAD7 and YAP1. The decreased stability of the SMAD7/YAP1 complex facilitates YAP1 translocation to the nucleus and results in the subsequent transcription of the downstream gene connective tissue growth factor (CTGF).